Reference
In 1975, the Government of India, in collaboration with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), launched the Crocodile Conservation Project in Bhitarkanika National Park, Odisha. The project will complete 50 years on 17 June 2024 on the occasion of World Crocodile Day 2024.
General facts about crocodiles
- Crocodiles generally inhabit tropical and subtropical regions.
- They live mainly in the warm regions of Central and South America, Africa, Asia, and Australia.
- All crocodiles are semiaquatic and are found in saltwater bodies of water as well as freshwater habitats such as rivers, lakes, wetlands.
- Crocodile is carnivorous animal, it mostly preys on fish, reptiles, birds or mammals depending on the species and age.
- These are nocturnal animals. They have poikilothermic characteristics, due to which they can control their body temperature to a limited degree.
- All crocodiles are tropical species which, unlike alligators, are very sensitive to cold.
Difference between crocodiles and alligators
- A crocodile's snout is long and V-shaped, while an alligator's snout is wide and U-shaped.
- Crocodiles prefer to live in saltwater near the beach, while alligators live primarily in freshwater environments.
- Alligators have webbed feet, while crocodiles have separate toes.
- Crocodiles are able to secrete excess salt from their bodies through glands on their tongues, but alligators are not.
- Crocodiles are found in various regions around the world, mainly in tropical and subtropical habitats, while there are two species of alligators: the American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis) and the Chinese alligator (Alligator sinensis).
|
The role of crocodiles in the ecosystem
- Crocodiles play an important role in the balance of nature and environment.
- They are apex predators in their ecosystem, controlling populations of other animals and maintaining biodiversity.
- However, crocodiles also face a number of threats, including habitat loss, poaching, and illegal trade for their skin and meat.
Also know this
- World Crocodile Day is celebrated on June 17 by the Belize-based Crocodile Research Alliance.
- The day is a global awareness campaign to highlight the plight of endangered crocodiles and alligators around the world.
- The Crocodile Research Coalition is a Belize-based non-profit organization founded in January 2016 that seeks to conserve crocodiles and their environments throughout Central America and the Caribbean to ensure the long-term sustainability of biodiversity in the region.
|
Crocodile Conservation Project of India
- The Crocodile Conservation Project was launched in 1975 in Bhitarkanika National Park, Odisha.
- Objective: The main objective of the crocodile conservation project was to protect the natural habitat of the animals and to quickly revive the population through captive breeding as the survival rate of crocodile babies was low in nature due to hunting.
- Success of the Project: The Crocodile Conservation Project has increased the crocodile population in India.
- According to the Reptile Census Report of the year 2024, there are 1,811 saltwater crocodiles in Bhitarkanika.
- Sudhakar Kar of Odisha, famous as 'Crocodile Man', has a major contribution in the success of the project.
Crocodiles found in India
- There are three main species of crocodiles in India:
-
- Salty or saltwater crocodile (Crocodylus porosus),
- Marsh crocodile (Crocodylus palustris)
- Alligator (Gavialis gangeticus)
- Salty crocodiles are found in only three places in India: Bhitarkanika, Sunderbans, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Many conservation programmes are being run successfully by the Indian Government for the protection of crocodiles, such as:
-
- Tikarpada Gharial Project, Baula Project in Dangamal, Crocodile Captive Breeding Project in Nandankanan, Magar Project in Ramtirtha etc.
Conservation status :
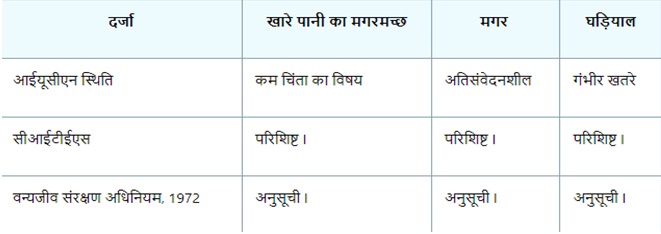
Species of Crocodiles in India
|
|

Mugger or marsh crocodile
(Crocodylus palustris)
|
Mugger or Marsh Crocodile:
- This is an egg-laying and hole-nesting species which is also considered dangerous.
- It is mainly restricted to the Indian subcontinent and is found in freshwater sources as well as coastal brackish water lagoons and estuaries.
- It is extinct in Bhutan and Myanmar.
- The major threats are destruction, fragmentation and alteration of habitats, fishing activities, and the use of crocodile parts for medicinal purposes.
|
|

Salty or Saltwater Crocodile
(Crocodylus porosus)
|
Estuarine or Saltwater Crocodile
- It is the largest living crocodile species on Earth, known globally as a known man-eater.
- This crocodile is found in the Bhitarkanika National Park in Odisha, Sundarbans in West Bengal and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- It is also found in South-East Asia and Northern Australia.
- The main threats to this species are poaching, habitat loss and hostility towards the species..
|
|

Crocodile
(Gavialis gangeticus)
|
Crocodile
- Also called gavials, these Asian crocodiles are distinguished from other crocodiles by their long, thin snout, which resembles a pot.
- The crocodile population is a good indicator of clean river water.
- It is known as a relatively harmless, fish-eating species.
- This species is mostly found in the fresh water of Himalayan rivers.
- The Chambal River in the northern slopes of the Vindhya Mountains (Madhya Pradesh) is known to be the primary habitat of the gharial.
- Other Himalayan rivers like Ghaghara, Gandak River, Girwa River, Ramganga River and Son River are its secondary habitats.
- The main threats to this species are illegal sand mining, poaching, increasing river pollution, dam construction, large-scale fishing and floods.
|
