Key Points:

- Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on Saturday (February 1) presented her eighth consecutive Union Budget.
- So far, schemes for the MSME sector, women and farmers have been announced.
- Her speech was expected to discuss issues such as economic growth, unemployment and relief to the middle class.
- A day earlier, the Economic Survey was tabled in Parliament, as has been the tradition.
- It projected a growth rate of 6.3-6.8 per cent for the next fiscal, saying, “Developed India@2047 envisions India as a developed nation by 2047, the centenary of our Independence.
- This would require economic growth of around 8 per cent every year for at least a decade.”
- The Finance Minister outlined the broad principles of developed India, which include:
a) Zero poverty;
b) 100 per cent access to good quality schooling;
c) Access to high quality, affordable and comprehensive healthcare;
d) 100 per cent skilled workforce with meaningful employment;
e) Seventy per cent women in economic activity; and
f) Farmers making our country the 'food basket of the world'.
The Union Budget highlighted agriculture, MSMEs, investment and exports, using it as fuel to drive reforms guided by the spirit of inclusiveness.
First Engine: Agriculture
- Pradhan Mantri Dhan-Dhanya Krishi Yojana:
- Scheme announced in partnership with States in 100 districts for enhancing agricultural productivity, crop diversification, storage, irrigation facilities and credit availability.
- Rural Prosperity and Resilience Programme:
- Multi-sectoral programme to strengthen skills, investment, technology and rural economy, with special focus on rural women, young farmers, small farmers and landless families.
- Self-reliance Mission in Pulses:
- A 6-year mission will be launched with special focus on tur, urad and lentil, offering procurement of pulses by NAFED and NCCF.
- Expanded Agriculture Measures:
- Comprehensive programmes for vegetables and fruits, National Mission on High Yielding Seeds, and a five-year mission for cotton productivity outlined.
- Kisan Credit Card:
- Loan limit from Kisan Credit Card increased from Rs 3 lakh to Rs 5 lakh under the Revised Interest Subsidy Scheme.

Second Engine: MSMEs
- MSMEs as the Second Power Engine:
- The Finance Minister termed MSMEs as the second power engine of growth as they contribute to 45% of exports.
- Increase in Investment and Turnover Limits for MSMEs:
- The investment and turnover limits for classification of MSMEs were increased by 2.5 and 2 times respectively.
- Increase in Credit Availability:
- Steps were taken to enhance credit availability for MSMEs with guarantee cover.
- New Scheme Announced:
- Term loans up to Rs 2 crore will be made available to 5 lakh women, Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes first-time entrepreneurs over the next 5 years.
- Scheme for Made in India Toys:
- The government launched a scheme to create a global hub for 'Made in India' branded toys.
- National Manufacturing Mission:
- The government announced setting up of a National Manufacturing Mission covering small, medium and large industries to promote "Make in India".
Third Engine: Investment
- Investment as the Third Engine:
- The Union Minister described investment as the third engine of growth, in which priority will be given to investment in people, economy and innovation.
- Atal Tinkering Labs:
- 50,000 Atal Tinkering Labs will be set up in government schools in the next 5 years.
- BharatNet Project:
- Under BharatNet, all government secondary schools and primary health centres in rural areas will be given broadband connectivity.
- Indian Language Book Scheme:
- The scheme will be implemented to make books in Indian languages available in digital form for school and higher education.
- Centres for Skill Development:
- Five National Centres of Excellence will be set up with the objective of "Building for India, Building for the World".
- Centres of Excellence in Artificial Intelligence:
- Centres of Excellence in Artificial Intelligence for Education will be set up with an outlay of Rs 500 crore.
- Identity Cards for Gig Workers:
- Identity cards for gig workers, registration on e-Shram portal and healthcare under PM Jan Arogya Yojana will be arranged.
- Infrastructure Projects in PPP Mode:
- Infrastructure Ministry announced to bring projects in PPP mode in a 3-year pipeline.
- Interest Free Loans to States:
- An outlay of Rs 1.5 lakh crore proposed for 50-year interest free loans to states.
- Second Asset Monetisation Scheme:
- Second Asset Monetisation Scheme announced to infuse Rs 10 lakh crore capital in new projects by 2025-30.
- Jal Jeevan Mission:
- Jal Jeevan Mission extended to 2028, with focus on quality infrastructure and rural piped water supply schemes through "Jan Bhagidari".
- Urban Challenge Fund:
- An Urban Challenge Fund of Rs 1 lakh crore will be set up, aimed at 'cities as growth hubs' and 'creative redevelopment of cities'.
- Investing in Innovation:
- Rs 20,000 crore allocated for private sector driven research, development and innovation.
- National Geospatial Mission:
- National Geospatial Mission proposed to develop basic geospatial infrastructure and data.
- Gyan Bharatam Mission:
- Gyan Bharatam Mission proposed to survey, document and preserve over 1 crore manuscripts.
- Digital Repository of Indian Knowledge Systems:
- Scheme to establish a National Digital Repository of Indian Knowledge Systems for knowledge sharing.
Fourth Engine: Exports
- Exports as the Fourth Engine:
- Smt. Sitharaman termed exports as the fourth engine of growth, and announced an Export Promotion Mission to help MSMEs make inroads into the export markets.
- Bharat TradeNet (BTN):
- Digital Public Infrastructure for International Trade ‘Bharat TradeNet’ (BTN) proposed as a unified platform for trade documentation and financing solutions.
- Integration to Global Supply Chains:
- Support will be provided to develop domestic manufacturing capacity to integrate the economy with global supply chains.
- Support to Industry 4.0:
- Government will support the domestic electronic equipment industry to take advantage of opportunities related to Industry 4.0.
- Promotion of Global Competence Centres in Tier 2 Cities:
- National framework proposed for promoting Global Competence Centres in emerging Tier 2 cities.
- Support to Perishable Horticultural Products:
- Support will be provided in upgradation of infrastructure and storage for air freight including high value perishable horticultural products.
Fiscal Consolidation
- Commitment to Fiscal Consolidation:
- The Union Finance Minister reiterated the commitment to remain on the path of fiscal consolidation.
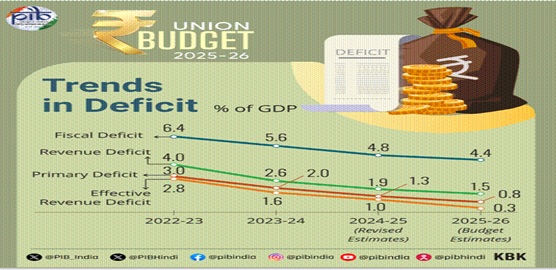
- Revised Estimates of Fiscal Deficit:
- Smt. Sitharaman said that the Revised Estimates of Fiscal Deficit for 2024-25 is 4.8 per cent of GDP.
- Budget Estimates 2025-26:
- As per the Budget Estimates, the fiscal deficit for 2025-26 is estimated to be 4.4 per cent of GDP.
- Detailed Roadmap:
- The detailed roadmap for the next 6 years is clearly laid out in the FRBM Statement.
Revised Estimates 2024-25
- The revised estimates of total receipts are ₹31.47 lakh crore, of which net tax receipts are ₹25.57 lakh crore.
- The revised estimates of total expenditure are ₹47.16 lakh crore, of which capital expenditure is ₹10.18 lakh crore.
Budget Estimates 2025-26
- For the financial year 2025-26, total receipts are estimated at ₹34.96 lakh crore and total expenditure at ₹50.65 lakh crore.
- Net tax receipts are estimated at ₹28.37 lakh crore.

Income Tax Proposals and New Tax Regime
|
How much has the new tax regime changed
|
|
Old slab
|
New slab
|
|
Income (in Rs lakh)
|
Tax (%)
|
Income (in Rs lakh)
|
Tax (%)
|
|
0 -3
|
0
|
0 - 4
|
0
|
|
3 - 7
|
5%
|
4 - 8
|
5%
|
|
7 - 10
|
10%
|
8 - 12
|
10%
|
|
10 - 12
|
15%
|
12 - 16
|
15%
|
|
12 - 15
|
20%
|
16 - 20
|
20%
|
|
More then 15
|
30%
|
20 - 24
|
25%
|
|
|
More then 24
|
30%
|
- New Income Tax Regime:
- No income tax on income up to ₹12 lakh per annum, salaried individuals earning up to ₹12.75 lakh will pay zero tax.
- Proposed Tax Slabs:
- Zero tax up to average income of ₹1 lakh, except for special rates of income.
- Revenue Loss:
- The new tax structure will lead to a revenue loss of about ₹1 lakh crore for the government.
Focus on middle class
- Personal Income Tax Reforms:
- Special focus on middle class, rationalization of TDS/TCS and encouragement of voluntary compliance.
- TDS/TCS Amendments:
- Tax deduction limit on interest for senior citizens increased from ₹50,000 to ₹1 lakh, TDS limit on rent from ₹2.4 lakh to ₹6 lakh.
- Voluntary Compliance:
- Time limit for filing updated returns for the assessment year increased from 2 to 4 years.
- Benefits to Small Charitable Trusts:
- Registration period increased from 5 to 10 years.
- Vivaad se Vishwas Scheme:
- Around 33,000 taxpayers availed it.
Trade and Investment Promotion
- International Transactions:
- Arms Length Pricing fixed for 3-year block period.
- Investment Boost:
- Incorporation period for start-ups extended to 5 years.
- Investment in Infrastructure:
- Date for investment in Sovereign Wealth Funds and Pension Funds extended to March 31, 2030.
Customs
-
- BCD Exemption:
- Customs duty exemption on life saving drugs, minerals, textile machinery.
- Domestic Production Boost:
- Exemption of capital goods for lithium-ion batteries and mobile phone battery manufacturing.
- Export Boost:
- BCD exemption on handicrafts, fish feed and other products.
- Facilitating Exports:
- Reduction in BCD on Wet Blue Leather and Frozen Fish Paste.





