| (Main Exam, General Studies Paper-3: Technology, Biodiversity, Environment, Security and Disaster Management, Conservation, Environmental Pollution and Degradation, Environmental Impact Assessment) |
Reference
A report by a joint committee constituted by the National Green Tribunal (NGT) has noted high levels of chromium contamination in groundwater in areas around Sukinda Valley, posing a serious health hazard.
About Chromium
- Chromium is a shiny and hard metal with a high melting point. Its colour is silver-grey. It is obtained from chromite ore.
- Its symbol is Cr and atomic number is 24. It is the third hardest element after carbon (diamond) and boron.
- There are mainly two types of chromium:
- Trivalent Chromium Cr(III)
- Hexavalent Chromium Cr(VI)
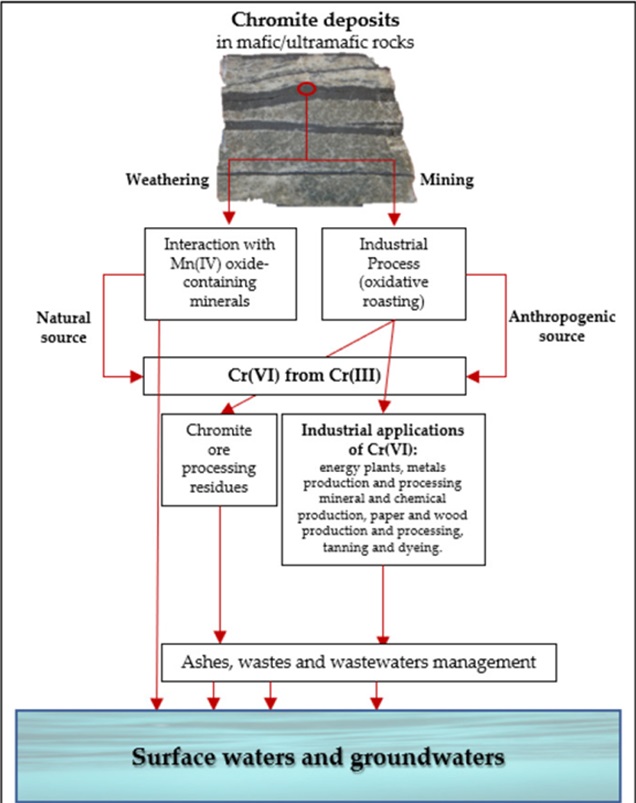
- Trivalent chromium Cr(III) is considered essential for a variety of organisms, including humans. It plays an important role in the metabolism of glucose, protein, and fats.
- Hexavalent chromium Cr(VI) is a highly toxic form of chromium that negatively affects human health as well as the environment and biodiversity. Cr(VI) is produced mostly by human activities.
What is chromium pollution?
- Chromium enters the environment through natural processes and anthropogenic activities, such as mining, smelting, metal processing, industrial production and agricultural activities.
- This results in pollution and destruction of the ecosystem.
- In India, states like Tamil Nadu (e.g. Ranipet), Uttar Pradesh (e.g. Kanpur), Odisha (e.g. Sukinda Valley) and West Bengal (e.g. Ranaghat-Phulia) are at high risk due to high concentrations of chromium in soil and water.
- Huge quantities of waste from open-cast chromite mining and quarrying operations are directly discharged into water bodies without any treatment.
Sukinda Valley Area
- Sukinda Valley is a mineral-rich area located in Jajpur district of Odisha. It is surrounded by the Mahagiri Range and Daitari Range.
- It is also known as the land of 'black diamonds' for its vast reserves of chromium. It has the world's largest open cast chromite ore mines.
- According to an Indian health group, diseases related to chromite pollution are a significant factor in the total deaths in mining areas.
- The city is also included in the list of most polluted cities in the world.
- 98.6% of the chromium reserves in India are found in the Sukinda region of Odisha.
|
Effects of Chromium Pollution
Effects on Human Health
- Hexavalent chromium Cr(VI) is considered a carcinogen, increasing the risk of lung cancer.
- Increased levels of chromium in aquatic ecosystems are responsible for eye damage, pulmonary damage, gastrointestinal abnormalities in humans.
- Skin contact with some hexavalent chromium compounds may cause skin ulcers and allergic reactions.
Effects on Agriculture
- Plants absorb hexavalent chromium Cr(VI) from the soil, which hinders their growth and development.
- Chromium exposure reduces soil fertility, which affects food production.
- It hinders crop growth and yield and can reduce their quality.
- According to several studies, chromium pollution negatively affects the metabolic activities of plants.
Impact on environment and biodiversity
- According to studies of the long-term toxicity of Cr(VI) on invertebrates, it enters the body of fish and has lethal effects on the liver and kidneys.
- According to several studies, its concentration in the environment, especially in surface water and groundwater, has increased beyond the prescribed limits.
- Cr(VI) directly or indirectly negatively affects terrestrial plants, aquatic phytoplankton and other organisms.
Solutions to Chromium Pollution
- Several strategies have been adopted for the removal of Cr-metal from contaminated sites, mainly focused on promoting green technologies through various chemical transformations, adsorption, oxidation-precipitation reactions. However, they have their own advantages and disadvantages:
- For example, chemical-based precipitation technologies have moderately high volumes of wastewater and sludge as by-products, resulting in increased operating costs due to their disposal through dehydration processes.
- Bioremediation is considered as a potential and environmentally friendly approach for the reduction or immobilization of pollutants through microorganisms.
- Some hyperaccumulator plant species significantly reduce Cr from polluted soil and water.
- Currently, nano-particles are emerging as an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional adsorbents. These nano-materials are being considered for the treatment of hazardous Cr containing wastewater.
Uses of Chromium
- Chromium is used extensively in mineral and chemical industries, welding industry and refinery industry.
- 94.5% of the total chromium in the world is used in mineral industry, 3.5% in refinery industry and 2% in chemical industry.
- Chromium is also used in iron, steel, cement, glass, ceramic industry, leather, paint, etc.
- Indian chromite reserves contribute about 2% of the total world resources.
|



