|
Preliminary Exam
(Defence Technology)
Mains Exam
(General Studies Paper-3 : Issues Related to Defence Technology)
|
Reference
Directed Energy Weapons have become an important part of India's elaborate security structure. However, no official announcement has been made in this regard.
What are Directed Energy Weapons?
- Directed energy weapons (DEW) use focused energy from electromagnetic or particle technology rather than kinetic energy to destroy targets.
- DEW have the capability to damage physical targets several kilometres away with high precision and accuracy.
Characteristics of directed energy weapons
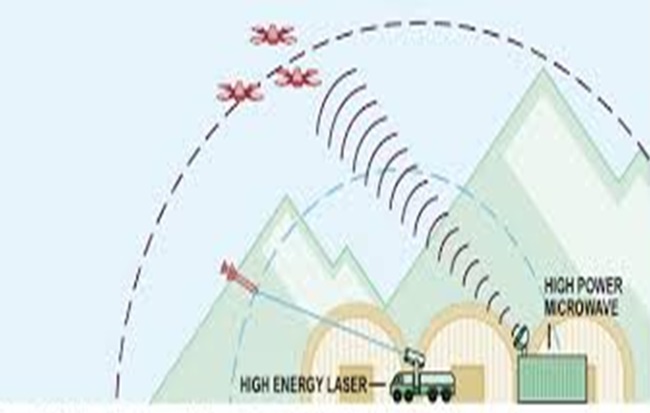
- High-Energy Lasers: High-energy lasers (HELs) have several significant advantages over conventional weapons, such as the ability to hit targets at the speed of light with precision and a virtually unlimited magazine.
- However, they can be adversely affected by conditions such as rain or fog.
- High-Power Microwaves: High-power microwave weapons (HPMs) have shorter ranges than HELs and lose power over longer distances, but they are not affected by weather and can strike targets over a wide area.
- Millimeter Waves: Millimeter wave-based directed energy weapons have many non-lethal military applications, including crowd control and interdiction areas.
- Particle Beam: Particle beam weapons have strong penetration capability, high speed and high energy and can operate in all weather conditions.
- However, this technology is extremely complex. It has to overcome many challenges before it can be used in warfare.
- Space: Applications of directed energy in the space sector are the focus of much research, including using directed energy to accelerate spacecraft, propulsion of satellites and intercepting, deflecting comets or asteroids that pose a threat to the Earth.
Global Scenario
- United States: DEW development in the US gained momentum in the 1980s, as part of the Strategic Defense Initiative aimed at developing laser weapons against Soviet missiles, later codenamed 'Star Wars'.
- China: China has been developing DEWs since the late 1980s and has reportedly developed the LW-30, a 30-kilowatt road-mobile HEL designed to counter unmanned aerial vehicles and guided weapons.
- Russia: It has been conducting DEW research since the 1960s, with a particular emphasis on HELs. It has reportedly deployed the Peresvet Ground-based HEL along with several mobile intercontinental ballistic missile units.
- United Kingdom: It successfully deployed its Dragonfire HEL weapon in January 2024.
- Israel: Following the October 7 attacks by Hamas, Israel has sought to accelerate the development of its Iron Beam laser weapon to boost the kinetic interceptors of its Iron Dome missile defense system.
- Countries such as France, Turkey, Iran, South Korea and Japan are also investing in their own DEW programs.
Indian Initiatives
- Although there has been no official announcement by the Indian Army, DEWs are believed to be a part of India’s security strategy.
- India’s foray into DEWs began primarily with a classified project called ‘Tri-Netra’, which was implemented by the Delhi-based Laser Science and Technology Centre (LASTEC).
- BEL(Bharat Electronics Limited) has successfully produced a 2 kilowatt (kW) laser-based DEW. It is aimed at countering new, asymmetric and disruptive threats like drones and unmanned aerial vehicles.
- Reports also suggest that products from classified programmes like KALI (Kilo Ampere Linear Injector) and DURGA (Directionally Unrestricted Ray-Gun Array) have already been inducted into the armed forces.


