Genes

Genes are segments of Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
DNA is an important nucleic acid found in human cells along with Ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Chromosomes are thread like structures made of protein and a single molecule of DNA.
Genome is the entire set of DNA instructions found in a cell.
|
Comparison between DNA and RNA
|
|
Standard
|
DNA
|
RNA
|
|
Structure
|
Double-stranded Helix
|
Single-stranded
|
|
Nitrogenous Bases
|
Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G)
|
Adenine (A), Uracil (U), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G)
|
|
Functions
|
Storage of genetic information for inheritance
|
Regulating gene expression and playing an important role in protein synthesis
|
Genome Editing
- Editing DNA can change physical characteristics (such as eye colour) and reduce the risk of certain diseases.
- Site-directed nucleases (SDNs) are used to make changes. In this:
- Nucleotides are added, deleted or replaced.
- Subsequent genome editing is effected by splitting the DNA strands.
Major technologies of genome editing
- CRISPR/Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats)
- Zinc Finger Nucleases (ZFN)
- Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALEN)
- Unlike Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs), under gene editing, modifications are made to the existing genetic material, while in GMOs, transgenes (foreign genes) are added.
CRISPR/Cas9 technology
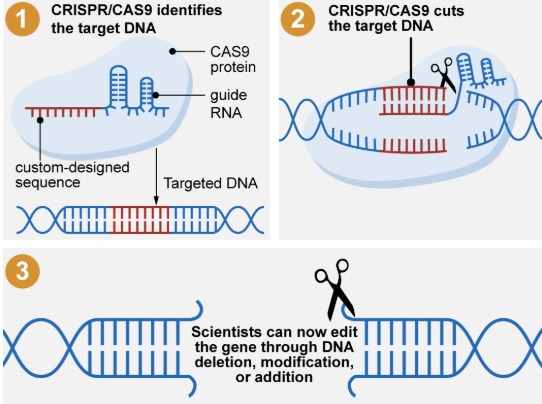
- The genetic code is changed or specific places of DNA are edited.
- It works on the "cut and paste" mechanism:
- The genetic code to be changed is determined.
- The Cas9 protein acts like molecular scissors and cuts the targeted section of DNA.
- Through this, the necessary changes are made in the genome.
Genome Sequencing
- Finding out the exact order of base pairs in the strand of DNA is called sequencing.
- Genetic diseases can be treated for predictive diagnosis and personalized healthcare.
- Applications of Genome Sequencing
- Predictive diagnosis and personalized healthcare Genetic diseases can be treated for this.
- Paternity testing: Biological relationships can be confirmed.
- Agriculture:
- Identification of high yield traits.
- Improvement of crops to increase disease resistance.
- Genetic improvement to increase climate resilience.
Micro RNA (miRNA) and Gene Regulation
What is micro RNA (miRNA)?
- Micro RNAs are small non-coding RNAs that help control gene expression in cells. They bind to mRNA and:
- Prevent translation of mRNA, which prevents protein formation.
- Completely destroy mRNA, which eliminates gene expression.
Gene Regulation: Mechanisms and Importance
- Gene regulation is the process by which cells control the expression of genes, making proper function, growth, and environmental adaptation possible.
- It acts at the transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and epigenetic levels.
Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
- In prokaryotes it occurs mainly through the operon model.
- The lac operon (inducible system): is activated in the presence of lactose.
- The trp operon (repressive system): is inactivated in high amounts of tryptophan.
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
- It is more complex and acts at different levels:
- Transcriptional: transcription factors and epigenetic modifications (DNA methylation, histone acetylation).
- Post-transcriptional: alternative splicing and RNA interference (miRNA, siRNA).
- Translational: mRNA stability and ribosome control.
- Post-translational: Protein modification (phosphorylation, ubiquitination).
Importance
- Helpful in cell differentiation and growth.
- Promotes environmental adaptation.
- Helps in prevention of diseases.
- Useful in biotechnology and medicine.
Gene Expression:
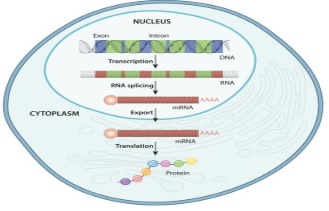
- Human body cells have chromosomes that contain similar gene sets.
- Gene regulation determines which cells will express which proteins.
- Example: Muscle cells, nerve cells, etc. produce specific proteins that enable them to perform their functions.
Importance and use of microRNA
- In understanding cellular development – it affects the self-renewal and differentiation of stem cells.
- In immune response – maintains balance between innate and adaptive immune systems.
- In Oncogenesis – prevents healthy cells from transforming into cancer cells.
- In disease diagnosis – especially helpful in the identification and treatment of cancer.
Reverse Transcriptase
- Reverse transcriptase is an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase, which creates DNA from RNA.
- This enzyme drives the reaction called "reverse transcription".
- Example: Some viruses (such as HIV) use reverse transcriptase to create DNA from RNA.
- Research has found that bacteria (Klebsiella pneumonia) use RNA for reverse transcriptase during virus infection.


