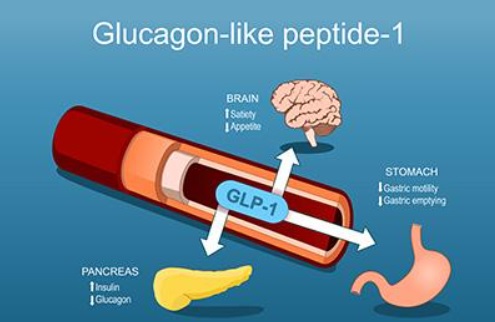
- Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) is an incretin hormone produced naturally in the human body.
- It plays a vital role in glucose metabolism, insulin regulation, and appetite suppression.
Sources of GLP-1 Production
GLP-1 is secreted by the following:
- Enteroendocrine L cells (Distal Gut – Small Intestine and Colon): The primary source of GLP-1 production.
- Pancreatic Alpha (α) Cells: Responsible for maintaining glucose homeostasis.
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Some neurons secrete GLP-1 to regulate appetite and food intake.
Mechanism of Action of GLP-1
- GLP-1 exerts its effects through multiple pathways:
Regulation of Blood Sugar Levels
- GLP-1 stimulates insulin secretion from the pancreas, lowering blood glucose levels.
- It inhibits glucagon secretion, preventing the liver from releasing excess glucose into the bloodstream.
Appetite Suppression
- GLP-1 acts on the hypothalamus (hunger centre of the brain), reducing food cravings.
- It promotes early satiety, helping in weight reduction.
Slowing of Gastric Emptying
- It delays the movement of food from the stomach to the intestines, prolonging the feeling of fullness.
- This reduces overall food intake and prevents overeating.
Cardiovascular and Metabolic Benefits
- GLP-1-based drugs improve heart health by reducing blood pressure and inflammation.
- They lower the risk of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases in diabetic and obese patients.
GLP-1-Based Weight Loss Medications
- Given its short half-life (a few minutes), natural GLP-1 is ineffective for sustained weight management.
- Hence, synthetic GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have been developed.
- These drugs have a longer duration of action and are widely used for weight loss and diabetes management.
List of GLP-1-Based Medications
|
Drug Name
|
Primary Use
|
Administration
|
|
Semaglutide
|
Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes
|
Weekly Injection
|
|
Liraglutide
|
Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes
|
Daily Injection
|
|
Dulaglutide
|
Type 2 Diabetes
|
Weekly Injection
|
|
Exenatide
|
Type 2 Diabetes
|
Twice-Daily Injection
|
|
Tirzepatide
|
Type 2 Diabetes, Weight Loss
|
Weekly Injection
|
Advantages of GLP-1-Based Drugs for Weight Loss
- Effective Appetite Control: Helps reduce calorie intake naturally.
- Sustained Weight Loss: Clinically proven to cause significant and long-term weight reduction.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Prevents spikes in blood sugar levels, beneficial for diabetics.
- Lower Risk of Heart Disease: Reduces cholesterol levels and improves cardiovascular health.
Challenges and Side Effects
- Despite their benefits, GLP-1 receptor agonists come with certain challenges:
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and constipation are common side effects.
- High Cost: These drugs are expensive and not easily accessible for the general population.
- Injection-Based Administration: Most GLP-1 drugs require subcutaneous (under-the-skin) injections, which may deter some users.
- Long-Term Safety Concerns: Studies are still ongoing regarding the long-term effects on kidney and thyroid function.
Comparative Analysis: GLP-1 vs. Traditional Weight Loss Methods
|
Factor
|
GLP-1 Drugs
|
Traditional Weight Loss Methods
|
|
Mechanism
|
Appetite suppression, glucose control
|
Diet and exercise
|
|
Effectiveness
|
Rapid and significant weight loss
|
Slow and gradual
|
|
Sustainability
|
Requires continuous use
|
Lifestyle-dependent
|
|
Side Effects
|
Nausea, vomiting, cost issues
|
Minimal
|
|
Accessibility
|
Prescription-based, expensive
|
Free or low-cost
|
GLP-1 and the Future of Obesity Treatment
- Emerging Research: Scientists are developing oral GLP-1 medications to replace injections.
- Combination Therapies: Research is ongoing to combine GLP-1 drugs with other obesity treatments for enhanced results.
- Personalized Medicine: Future treatments may involve customized GLP-1 therapies based on genetic profiles.


