|
Syllabus: Prelims GS Paper I : Current Events of National and International Importance; Economic and Social Development-Sustainable Development, Poverty, Inclusion, Demographics, Social Sector Initiatives, etc.
Mains GS Paper II : Issues Relating to Development and Management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
|
Context
Shutdown of all educational institutions due to the rapid spread of coronavirus in the country has impacted the entire education sector in India.
Background
The education sector is facing unprecedented challenges and needs to adapt and find solutions to keep students motivated and in their route to learning. The education sector and educators deal to overcome these challenges by innovating ideas and try to find the ways for students to continue to learn.
In Detail
The COVID-19, is leaving a lasting impression on education system around the world. Students are naturally the worst affected among education sector stakeholders. It caused an interruption to their learning journey. And in the case of dropouts, it was the final straw for at-risk children who struggled to get an education at the best of times. Though the Indian government spends 4.6 percent of its GDP on education, this is lower than in sub-Saharan countries like Kenya, Togo, and Zimbabwe.
In a larger perspective it has also raised the spectre of educational institutions shuttering their doors completely or taking unprecedented steps that have invariably affected jobs and livelihoods.
The structure of schooling and learning, including teaching and assessment methodologies, was the first to be affected by these closures. Only a handful of private schools could adopt online teaching methods. Their low-income private and government school counterparts, on the other hand, have completely shut down for not having access to e-learning solutions. The students, in addition to the missed opportunities for learning, no longer have access to healthy meals during this time and are subject to economic and social stress.
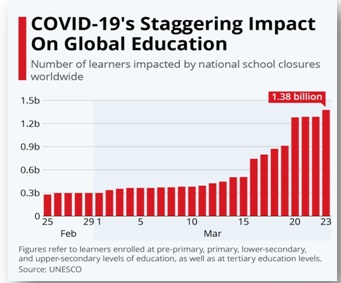 The pandemic has significantly disrupted the higher education sector as well, which is a critical determinant of a country’s economic future. A large number of Indian students just after the China has enrolled in foreign universities, especially in countries worst affected by the pandemic, the US, UK, Australia and China. Many such students have now been barred from leaving these countries.
The pandemic has significantly disrupted the higher education sector as well, which is a critical determinant of a country’s economic future. A large number of Indian students just after the China has enrolled in foreign universities, especially in countries worst affected by the pandemic, the US, UK, Australia and China. Many such students have now been barred from leaving these countries.
The bigger concern, however, on everybody’s mind is the effect of the disease on the employment rate. Recent graduates in India are fearing withdrawal of job offers from corporates because of the current situation. The Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy’s (CMIE) estimates on unemployment shot up from 8.4% in mid-March to 23% in early April and the urban unemployment rate to 30.9%.
Immediate Steps to Maintain Continuity
Open-source digital learning solutions and Learning Management Software should be adopted so teachers can conduct teaching online. The DIKSHA platform, with reach across all states in India, can be further strengthened to ensure accessibility of learning to the students.
Inclusive learning solutions, especially for the most vulnerable and marginalized, need to be developed. With a rapid increase of mobile internet users in India, which is expected to reach 85% households by 2024, technology is enabling ubiquitous access and personalization of education even in the remotest parts of the country. This can change the schooling system and increase the effectiveness of learning and teaching, giving students and teachers multiple options to choose from. Many aspirational districts have initiated innovative, mobile-based learning models for effective delivery of education.
Strategies are required to prepare the higher education sector for the evolving demand–supply trends across the globe—particularly those related to the global mobility of students and faculty and improving the quality of and demand for higher studies in India. Further, immediate measures are required to mitigate the effects of the pandemic on job offers, internship programs, and research projects.
It is important to reconsider the current delivery and pedagogical methods in school and higher education by seamlessly integrating classroom learning with e-learning modes to build a unified learning system. Further, it is also important to establish quality assurance mechanisms and quality benchmark for online learning developed and offered by India HEIs as well as e-learning platforms (growing rapidly).
Indian traditional knowledge is well known across the globe for its scientific innovations, values, and benefits to develop sustainable technologies and medicines. The courses on Indian traditional knowledge systems in the fields of yoga, Indian medicines, architecture, hydraulics, ethnobotany, metallurgy and agriculture should be integrated with a present-day mainstream university education to serve the larger cause of humanity.
The corporate model addresses not just financial sustainability but also a professional governance structure that would entail better accountability and holistic education.
Conclusion
Needless to say, the pandemic has transformed the centuries-old, chalk & talk teaching model to the one driven by technology. This disruption in the delivery of education is pushing policymakers to figure out how to drive engagement at scale while ensuring inclusive e-learning solutions and tackling the digital divide.
Many e-learning platforms offer multiple courses on the same subjects with different levels of certifications, methodology and assessment parameters. So, the quality of courses may differ across different e-learning platforms.
The Future Education system will not only decide the fate of the academic sector in India but also its quality, ranking, research, innovation potential and its collective impact on our country’s economy.
Connecting the Article
Question for Prelims
Which one of the following Mobile App is not related to the e-Learning ?
(a) DIKSHA
(b) SWAYAM
(c) SWAYAM PRABHA
(d) None of the above
Question for Mains
E-learning platforms have emerged as one of the best measures to help the students continue their studies during COVID-19 outbreak. Discuss.

 Contact Us
Contact Us  New Batch : 9555124124/ 7428085757
New Batch : 9555124124/ 7428085757  Tech Support : 9555124124/ 7428085757
Tech Support : 9555124124/ 7428085757








