|
Syllabus: Prelims GS Paper I : Current Events of National and International Importance.
Mains GS Paper II : Bilateral, Regional and Global Groupings and Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
|
Context
India and the US are close to inking a quick trade deal, similar to Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA), The pact aims to resolve pending issues over the past couple of years.
Background
India, one of the world's largest consumers of dairy products, has offered an opening to US dairy imports through a quota-based system. These products would need a certificate they are not derived from animals that have consumed feeds that include internal organs, blood meal or tissues of ruminants because of religious sensibilities in India. In addition to luring American dairy producers, India has offered to roll back tariff hikes on almonds, walnuts and apples.
Last year, trade tensions culminated in the US revoking India’s status as a beneficiary of its Generalised System of Preferences (GSP) programme that allowed duty-free benefits to export a variety of products. India responded by implementing retaliatory tariffs on 28 items imported from the US, including apples and almonds. It is the world's largest buyer of US almonds, and second largest for its apples.
Importance of India-US Trade Deal
Last year, India decided not to join Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), pressure has on itself to strengthen existing separate trade agreements. In the backdrop of the global economic slowdown, where India’s global exports have fallen consistently, it is important for the country to diversify and strengthen bilateral relations with other markets.
In the ongoing conflict, it is important for India to divert its trade from China to other trusted allies including the US.
The US is India’s largest trading partner, with bilateral trade touching $88.75 billion in the 2019-2020 financial year.
India is among the countries that exported more to the United States than it imported, and the US is facing a trade deficit of over $21 billion in 2017-18.
Issues of Contention
The Harley Tariffs
US is continiously complaining on the tarrif rates imposed by the India on Haeley Davidson bikes. Even after India halved the duty on the bike to 50% in 2018, US has said the rate is still unacceptable.
Steel industry hit
In 2018, the US imposed additional tariffs of 25% on steel and 10% on aluminum imports from various countries, including India. In March 2018, India challenged the US decision at the World Trade Organization (WTO). India held off on imposing retaliatory tariffs until the US struck again by removing it from a scheme of preferential access to the American market.
|
Generalised System of Preferences (GSP)
The GSP is largest and oldest US trade preference programme, designed to promote economic development by allowing duty-free entry for thousands of products from designated beneficiary countries.
|
Generalised System of Preferences (GSP)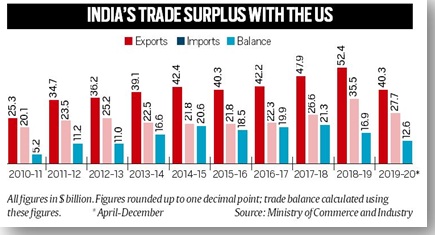
In June 2019, the US terminated India’s benefits under the GSP scheme, which provides preferential, duty-free access for over $6 billion worth of products exported from this country to the US.
India was the largest beneficiary of the US GSP programme. Removal from the GSP list amidst rising trade tensions prompted India to finally impose retaliatory tariffs on several American imports, including almonds, fresh apples, and phosphoric acid, the US approached the WTO against India. The USTR classified India as a “developed” country based on certain metrics.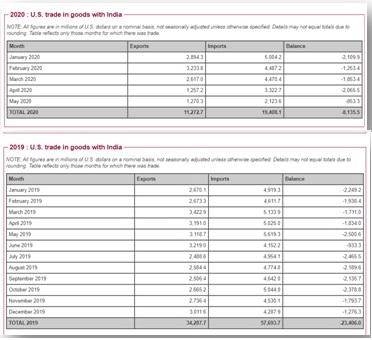
Farms, Medical Devices
The US has long demanded greater access for American agriculture and dairy products. For India, protecting its domestic agriculture and dairy interests was a major reason to walk out of the RCEP agreement.
India has imposed nominal cess on imported medical devices, though India has decided to apply trade margin on coronary stents and knee implants at the first point of sale (price to stockiest).
India's Steps to Remove Deadlock
While the United States is among India’s top trading partners for goods, India is its eighth largest. India’s trade surplus with the US came down to $16.9 billion in 2018-19, and surplus could be reduced further through imports of products such as aircraft from American firms.
This deal is expected to be almost evenly balanced in terms of trading value for both the partners and could be followed by talks on a potential free trade agreement (FTA).
As part of the limited deal, India will likely reduce tariffs on high-end bikes like Harley Davidson, pledge greater market access in farm products, including cherry, and sweeten its initial offer on easing price caps in medical equipment.
If the US agrees to roll back its extra tariff of 25% on Indian steel and 10% on Aluminum, New Delhi will lift retaliatory steps and scrap punitive duties on 29 American goods, including farm items like almond, apple and walnut.
However, negotiations on the American demand for India to scrap duties on seven ICT products, including high-end phones and smart-watches, are yet to be concluded. New Delhi had estimated that any such move would mean a potential customs revenue loss of $3.2 billion or more a year. Instead, India offered to trim tariffs on those ICT products which could potentially benefit the US more, without causing it such a big revenue loss.
Stringent US patent protection laws and various steps by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have dented India’s exports of pharmaceutical products. This is among the important non-tariff barriers that India wants the US to remove.
Conclusion
Experts feel that India and the US could begin with some “low-hanging fruit” to indicate their willingness for a deeper economic commitment. This includes the US reinstating India’s benefits under the GSP programme, and India doing away with duties on motorcycles.
Also, India should look at an early harvest in the form of a PTA rather than waiting for the gains of FTA, which may take several years in finalization. India could look at an early harvest of maybe 50 or maybe 100 products and services, where we can engage with mutual trust and an open spirit, so that the partnership between the US and India can speed up at much faster pace.
Connecting the Article
Question for Prelims
In context of Generalised System of Preferences, consider the following statements:
1. It is a trade preference programs offered by the ASEAN group.
2. India is the largest beneficiary of this program.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct ?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Question for Mains
How is promoting Indo-US trade beneficial for the Indian economy? Will it help in realizing India's dream of becoming a five trillion economy?

 Contact Us
Contact Us  New Batch : 9555124124/ 7428085757
New Batch : 9555124124/ 7428085757  Tech Support : 9555124124/ 7428085757
Tech Support : 9555124124/ 7428085757










