

Context: A new study has found that the diet of people from the Indus Valley civilization was dominated by meat.
 Background: In a new study, it was revealed that the diet of people from the ancient Indus Valley civilization was dominated by meat. The study published in Journal of Archaeological Science has shown that apart from cultivating and growing crops, the civilization also used to eat meat. In fact, experts assume that the tandoori roti and chicken may have first come from the Indus Valley civilization.
Background: In a new study, it was revealed that the diet of people from the ancient Indus Valley civilization was dominated by meat. The study published in Journal of Archaeological Science has shown that apart from cultivating and growing crops, the civilization also used to eat meat. In fact, experts assume that the tandoori roti and chicken may have first come from the Indus Valley civilization.
The study has found that the diet was dominated by meat of animals like pigs, cattle, buffalo and goat. Dairy products were also used in the civilization which is lies in northwestern India and is currently part of Haryana and Uttar Pradesh.
In Detail
The study, titled Lipid residues in pottery from the Indus Civilisation in northwest India, led by Akshyeta Suryanarayan as a part of her PhD programme, looks at the food habit of the people of that era on the basis of lipid residue analysis found in pottery from Harappan sites in Haryana.
The diet of the people of Indus Valley civilisation had a dominance of meat, including extensive eating of beef, revealed in a new study published in the ‘Journal of Archaeological Science’.
It finds dominance of animal products such as meat of pigs, cattle, buffalo, sheep and goat, as well as dairy products, used in ancient ceramic vessels from rural and urban settlements of Indus Valley civilisation in northwest India, includes Haryana and Uttar Pradesh.
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation is also called the Harappan culture. Archaeologists use the term “culture” for a group of objects, distinctive in style, that are usually found together within a specific geographical area and period of time. In the case of the Harappan culture, the distinctive objects include seals, beads, weights, stone blades and even baked bricks were found.
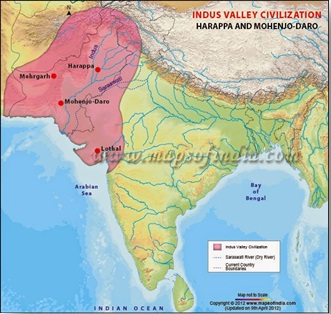
Indus Valley Civilization developed on the banks of the Indus river (ancient Saraswati river). Hadappa, Mohenjodado, Kalibanga, Lothal, Dholavira and Kharigadi were its main centers. It was spread over Pakistan, Northwest and parts of Western India and Afghanistan.
The first site where a unique culture was discovered, the civilisation is dated between c. 2600 and 1900 BCE. There were earlier and later cultures, often called Early Harappan and Late Harappan, in the same area. The Harappan civilisation is sometimes called the Mature Harappan culture to distinguish it from other cultures.
Harappa and Mohenjo-daro
The Indus civilization is known to have consisted of two large cities, Harappa and Mohenjo-daro, and more than 100 towns and villages, often of relatively small size.
It is beleived that Harappa succeeded Mohenjo-daro, which is known to have been devastated more than once by exceptional floods. The southern region of the civilization, on the Kathiawar Peninsula and beyond, appears to be of later origin than the major Indus sites. The civilization was literate, and its script, with some 250 to 500 characters, has been partly and tentatively deciphered, the language has been indefinitely identified as Dravidian.
Important Sites of Indus Valley Civilization
1. Harappa in western Punjab, near river Ravi
2. Mohenjodaro in Sindh, near river Indus
3. Sutkagendor in Baluchistan, near river Dashta
4. Rangpur in Ahmedabad, near river Meedar
5. Kalibangan in Ganganagar, near river Ghaggar
6. Lothal in Ahmedabad, near river Sabarmati
7. Banawali in Hissar, near river Saraswati
Agricultural In The Civilization
Representations on seals and terracotta sculpture indicate that the bull was known, and archaeologists extrapolate from this that oxen were used for ploughing. Moreover, terracotta models of the plough have been found at sites in Cholistan and at Banawali (Haryana).
Archaeologists have also found evidence of a field at Kalibangan (Rajasthan), associated with Early Harappan levels. The field had two sets of furrows at right angles to each other, suggesting that two different crops were grown together. Archaeologists have also tried to identify the tools used for harvesting.
Most Harappan sites are located in semi-arid lands, where irrigation was probably required for agriculture. Traces of canals have been found at the Harappan site of Shortughai in Afghanistan, but not in Punjab or Sind.
Decline of Indus Valley Civilization
There are different views of the historians on the decline of the civilization, like according to the Wheeler, Aryan attack was the main cause of the decline of the civilization. While the James Marshall stated that the natural calamities were responsible for the decline. The James Marshall theory is widely accepted.
Outlines of the Study
This study is concentrates on five villages, namely Alamgirpur (Meerut, UP), two in Masudpur (Hisar, Haryana), Lohari Ragho (Hisar), Khanak (Bhiwani, Haryana), also the Farmana town (in Rohtak district) and Rakhigarhi city (Hisar). Researc and analysis was conducted on 172 pottery fragments recovered from the sites.
The study says, that ceramics are one of the most ubiquitous artefacts recovered during archaeological excavations of proto and historic South Asian sites. Between 2600–1900 BC, five Indus Civilisation settlements developed into sizable cities, with a range of other medium-sized urban settlements, small settlements with specialised craft production and fortifications as well as rural settlements.
The study further talks of a diversity of plant products and regional variation in cropping practices. Both summer and winter-based cropping was practiced. Evidence of barley, wheat, rice, different varieties of millets, a range of winter and summer pulses, oilseed and fruit and vegetables, including brinjal, cucumber, grapes, date palm were grown and consumed.
Conclusion
There have been many studies on the food habits in Indus Valley civilizations before, but the latest study revealed the most surprising fact of the civilization. The latest study has opened a large scope of further studies on the ancient civilization. It is a further submission of the last study, which discovered the dairy products were being produced by the Harappans as far back as 2500 BCE.
Connecting the Article
Question for Prelims : With reference to the Indus Valley Civilization, consider the following statements:
1. Kalibangan was more planned and organized than Mohenjodaro.
2. Dockyards were found at the Lothal site.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct ?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Question for Mains : Discuss the important features of the Indus Valley Civilization.

Our support team will be happy to assist you!
