Why in the NEWS?
- Researchers at the University of Minnesota and the Midwest Antiviral Drug Discovery (AViDD) Centre have developed the first Nano-body-based inhibitors targeting the Ebola virus.
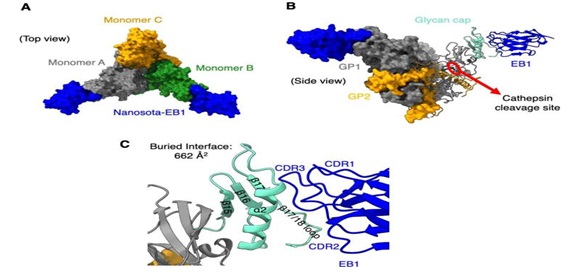
Key Points:
- Researchers at the University of Minnesota and the Midwest Antiviral Drug Discovery (AViDD) Center have developed the first Nano-body -based inhibitors targeting the Ebola virus, including two new Nano-body inhibitors – Nanosota-EB1 and Nanosota-EB2.
- These Nano-bodies help prevent the spread of the virus by targeting different parts of the virus.
What will you read next in this topic?
- What are Nano-bodies?
- Examples of Nano-body Uses
- What is the Ebola virus?
What are Nano-bodies?
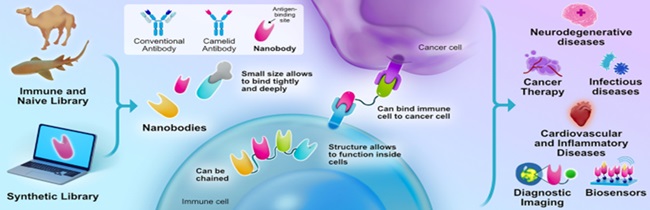
- Nano-bodies are small and specific types of antibodies that are specifically derived from alpacas and other camelid family animals such as camels and llamas.
- They are also called Camelid domain antibodies because their source is from the camelid family.
Key properties of Nano-bodies:
- Small in size:
- The size of Nano-bodies is much smaller than the antibodies produced by normal humans.
- Compared to a normal human antibody, the size of a Nano-body is about 1/10th.
- Due to this small size, they can easily enter even the difficult parts of the body where larger antibodies cannot reach.
- Specific targeting ability:
- Nano-bodies, like larger antibodies, react against specific antigens.
- They very specifically recognize a small and important part of a virus or pathogen.
- Due to this feature, they target very precisely, so that other healthy cells are not harmed during treatment.
- Stability and long-term effectiveness:
- Nano-bodies are very stable even in high temperatures and harsh environmental conditions.
- Unlike normal antibodies that are easily destroyed due to their protein structure, Nano-bodies remain very stable and remain effective for a long time.
- In addition, Nano-bodies can be preserved even in harsh conditions and there is no reduction in its effectiveness.
- Easy to manufacture:
- They can be prepared in less time and with fewer resources.
- In comparison, the manufacture of conventional antibodies is more expensive and time-consuming.
- Use in humans:
- Nano-bodies can be used in human treatments, especially in diseases that require attacking specific targets.
- For example, it can be effective in treating diseases like Ebola virus, COVID-19 and cancer.
- Multipurpose Uses:
- Nano-bodies can be used in diagnostics, therapeutic, and prophylactic measures.
- This means that Nano-bodies can be useful not only in treatment but also in the early diagnosis and prevention of diseases.
- Inflammation and Immune Response:
- After Nano-bodies bind to specific antigens, they help control the inflammatory response and other immune system reactions, thereby strengthening the body’s own defence system.
- Effective in Laboratory:
- Nano-bodies are used in various lab tests and biological studies.
- They have been found to be particularly effective against viruses and bacteria, such as COVID-19, Ebola, and other viruses.
Examples of Nano-body Uses
Use in COVID-19:
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers developed Nano-bodies against COVID-19.
- The purpose of these Nano-bodies was to bind to the virus's spike protein and prevent it from attaching to human cells.
Ebola Virus:
- Nano-bodies were used to stop the Ebola virus.
- Researchers developed inhibitors such as Nanosota-EB1 and Nanosota-EB2, which prevent the virus from entering and spreading inside the cell.
Cancer:
- Nano-bodies can also be used in cancer treatment.
- Due to its small size, it can directly reach tumour cells and treat them by targeting drugs or radiation there.
Use in Diagnostics:
- Nano-bodies are also used to identify various bacteria and viruses.
- They are extremely accurate and can provide test results quickly.
What is the Ebola virus?

- The Ebola virus is a highly contagious and deadly virus that causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD).
- The virus can cause severe bleeding, fever, and organ failure in humans and other primates (such as monkeys and gorillas).
- The case fatality rate is around 50%, but it can vary in different outbreaks, sometimes as high as 90%.
Type of virus:
- The Ebola virus is a member of the Filoviridae family, characterized by long, thread-like shapes.
- There are different types, including Ebola-Zaire, Sudan, Tanzania, and Marburg.
- The Zaire virus is the most deadly of these.
Mode of transmission:
- The Ebola virus is primarily spread through contact with the blood or other body fluids (such as sweat, faces, and excrement) of an infected person or animal.
- The virus enters the body through contact with an infected person or animal. Additionally, contact with contaminated surfaces or objects can also spread the virus.
- The initial symptoms of Ebola infection are flu-like, including:
- Fever, Headache, Muscle pain, Sore throat, Weakness, Vomiting, Diarrhea, Skin rash, Haemorrhage (bleeding) and organ failure.
Treatment:
- There is no specific treatment or vaccination for the Ebola virus, but supportive care is used for treatment, which includes replacing fluids, electrolytes, blood supply, and other medical measures.
- However, vaccines and treatments have been developed for Ebola in recent years, such as rVSV-ZEBOV (which is effective against Ebola).
Outbreaks and spread:
- The Ebola virus spreads in parts of Africa as outbreaks. The largest outbreak was in 2014-2016, which was in West Africa and infected thousands of people.
- The virus usually spreads from wild animals, especially bats and infected animals (such as monkeys).
Prevention:
- The best treatment for Ebola is prevention, such as avoiding contact with infected people, isolating infected patients, and staying away from contaminated objects.
- Hygiene, use of personal protective equipment such as masks and safety measures are essential for disease control.
|
Q. What are the names of the two new Nano-body inhibitors targeting the Ebola virus?
(a) NanoSota-EB1 and NanoSota-EB2
(b) NanoVira-EV1 and NanoVira-EV2
(c) NanoStop-EB1 and NanoStop-EB2
(d) EbolaNanos-1 and EbolaNanos-2
|



