(MAINS GS 3 : Science and Technology: Recent developments and their applications and effects in everyday life)
Context:
- Recently a research published in the journal Angewandte Chemie shows that researchers from the University of Massachusetts designed a type of nanoparticle which embodies a new approach to treating diseases like pancreatic cancer that could potentially revolutionise the field.
Targeted drug delivery:
- The new approach combines concepts of biologics and antibody–drug conjugates to produce protein–antibody conjugates that can be used for targeted drug delivery for example in case of pancreatic cancer.
- The team has tested the mechanism in cell lines in the lab and now plans to move on to studying it in mouse models.
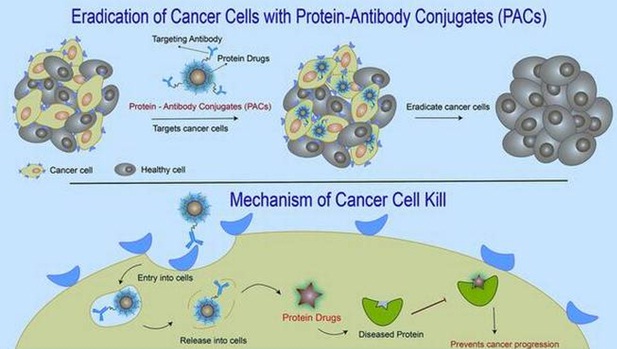
The two approaches:
- The new concept, namely, Protein–Antibody Conjugates or PACs, combines two different approaches to drug delivery.
- One is biologics, where the idea is to target a defective protein in the system by delivering proteins to it.
- An example of this is the case of insulin treatment where if a person is short of insulin, which is a protein, they are given a shot of this protein which balances the system.
Antibody conjugates
- The other concept is of using antibodies for drug delivery.
- Antibodies are something the body produces to detect a foreign substance inside the body.
- Antibodies can be developed to recognise anything that does not belong in our bodies including cancer cells as well.
- If there is something different on the surface of a cancer cell compared to a healthy cell, an antibody can be designed that selectively goes to the cancer cell.
- Drug molecules can be attached to the antibody, forming drug–antibody conjugates.
- Researchers developed protein–antibody conjugates or PACs, which have a protein attached to the antibody, and this conjugate can zero in on pancreatic cancer cells.
Undruggable cases:
- 90% of pancreatic cancers are undruggable as researchers till now do not know how to design drugs that will bind these cancerous cells.
- But with proteins, molecules can be designed that will bind to the target cells.
- In telling analogy, researchers compare the protein–antibody conjugate to an addressed envelope containing the drug.
- The antibody plays the role of the address and indicates the cell where the drug should precisely be delivered.



