Prelims: GDP growth rate
Mains: General Studies Paper-3, Indian economy and planning, topics related to mobilization of resources, progress, development and employment. |
Why in the NEWS?
- The central government has released the latest estimates of India's gross domestic product (GDP), with significant revisions for previous quarters and years.

Key Points:
- The GDP growth rate had fallen to 5.4% in the second quarter (July-September) of the current financial year (FY25), leading to a sharp decline in the economic growth rate.
- However, it was later revised to 5.6% in the revised estimate. The GDP data released for the third quarter (October-December) shows a growth rate of 6.2%.
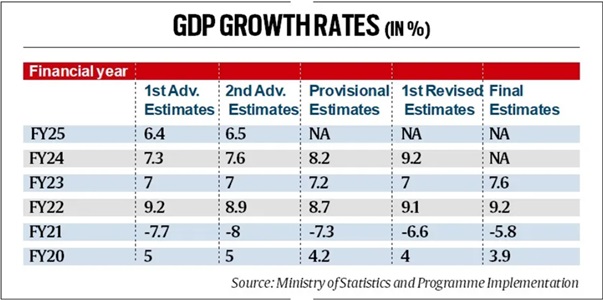
- The GDP growth for FY 2023-24 was raised from 8.2% to 9.2%, while for FY 2022-23 it was raised from 7% to 7.6%.
What will you read next in this topic?
- Reason for GDP Estimate Revision
- Impact of revised GDP data
- Factors affecting the economy
- What are GDP, NDP, GNP and NNP?
Reason for GDP Estimate Revision
- The government updates GDP estimates at various stages as data collection improves. The major stages in revising GDP estimates are as follows:
- First Advance Estimates (FAE) - It is released in January and estimates GDP based on initial data.
- Second Advance Estimates (SAE) - Released in February, incorporates additional data.
- Provisional Estimates (PE) - Published in May and contains detailed data for the entire financial year.
- First Revised Estimates (FRE) - Released a year later in February, incorporates more accurate data and economic surveys.
- Final Estimates - Released two years later in February, with the most comprehensive and updated data.
Impact of revised GDP data
The revised GDP data has provided several important economic insights:
- The economy was in better shape than previous estimates –
- The actual growth of the economy in FY23-24 was 9.2%, higher than the earlier estimated 8.2%.
- This shows that the economy was stronger than estimated and was performing better across sectors.
- The decline in the current growth rate is steeper than previously thought –
- The growth rate has now declined from 9.2% to 6.5%.
- This means that economic activity has slowed down more than expected, which may impact employment, investment and consumption.
- Doubts raised over the state of the economy –
- Heavy revisions in data may affect the credibility of official estimates.
- It is important for investors and policymakers to be cautious about the accuracy of these data and their interpretation.
Factors affecting the economy
- Growth in private consumer demand –
- Earlier it was estimated to grow at 4%, but after revision it was estimated to be 5.6%.
- This indicates that consumer spending was faster than expected.
- Private sector investment remained slow –
- The pace of investment in new production capacity remained sluggish, which affected the expansion plans of industries.
- Change in government expenditure –
- Government spending increased, but its contribution was not at the expected level.
- This suggests that the impact of government policies needs to be re-evaluated.
- Global economic uncertainty –
- The decline in external demand and fear of a global recession are impacting the Indian economy.
- This is a matter of concern especially for export-based sectors.
What are GDP, NDP, GNP and NNP?
- In economics, various indicators are used to measure the economic activities of a country.
- GDP, NDP, GNP and NNP are four important macroeconomic indicators of the economy.
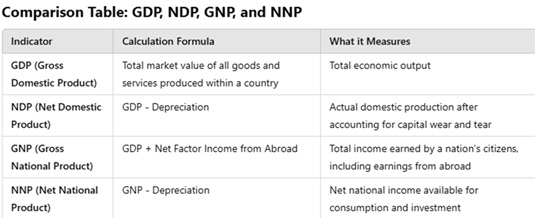
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- GDP is the total market value of all goods and services produced within the geographical boundaries of a country in a given period (quarterly or annually).
Methods of calculating GDP:
- GDP is calculated by three methods:
- Production Method – By assessing the total value of all goods and services produced in the country.
- Income Method – By adding up the total income (such as salary, profit, rent, interest) earned by all individuals and companies.
- Expenditure Method – By adding up consumer expenditure, government expenditure, investment and net exports (exports – imports).
- Types of GDP:
- Nominal GDP: GDP measured at current prices, which includes the effect of inflation.
- Real GDP: GDP adjusted by removing the effect of inflation.
Net Domestic Product (NDP)
- NDP is obtained by subtracting depreciation from GDP. Depreciation means the declining efficiency of machines, equipment and capital goods over time.
Calculation formula:
NDP= GDP − Depreciation
- It measures the real production capacity of the economy.
- By subtracting depreciation, it provides an accurate depiction of economic activity.
Gross National Product (GNP)
- GNP is an expanded version of GDP, which includes the total income earned by the citizens and companies of the country, whether within the country or abroad.
Calculation formula:
GNP= GDP + Income received from abroad − Income given to foreigners
- It shows the total income earned by the citizens of a country, regardless of where they are working.
- If a country earns more income from foreign investment, then GNP will be more than GDP.
Net National Product (NNP)
- NNP is obtained by subtracting depreciation from GNP.
Calculation formula:
NNP = GNP − Depreciation
- It provides an accurate measure of the total national income of a country.
- It is used in policy making, as it shows the real growth of the economy.
|
Q. What does GDP measure?
(a) Total income earned by a country's citizens, including abroad
(b) Total market value of all goods and services produced within a country
(c) The difference between exports and imports
(d) The net value of capital depreciation
|


