Syllabus: Mains GS Paper I : Important Geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclone etc.
Context
Delhi-NCR has witnessed more than 10 mild earthquakes since May which raised a binary speculation of either a big earthquake in near future or reduction in risk of an intense earthquake due to dissipation of energy through these low intensity tremors.
About Earthquake
- An earthquake is an intense shaking of earth’s surface. The shaking is caused by lithospheric plate movements in Earth’s outermost layer.
- It occurs when rocks break and slip along a fault in the earth.
- Energy is released during an earthquake in several forms such as movement along the fault, as heat, and as seismic waves that radiate out from the "focus" in all directions and cause the ground to shake, sometimes hundreds of kilometers away.
Where do earthquakes occur?
- Earthquakes occur all over the world; however, most occur on active faults that define the major tectonic plates of the earth.
- 90% of the world's earthquakes occur along these plate boundaries (that represent about 10% of the surface of the earth).
- The "Ring of Fire" encircling the Pacific Ocean is one of the most active areas in the world.
Can an Earthquake be predicted?
- Scientists say that the Himalayan region is due for a big earthquake, of magnitude 8 or even higher. That is because they have been able to measure the energy that is getting trapped under the surface as a result of one tectonic plate trying to move beneath the other one.
- But even here, scientists have no idea when this big earthquake will occur. The prediction about the big one is based only on the estimate of the energy that is ready to be released.
Why is Delhi-NCR prone to earthquakes ?
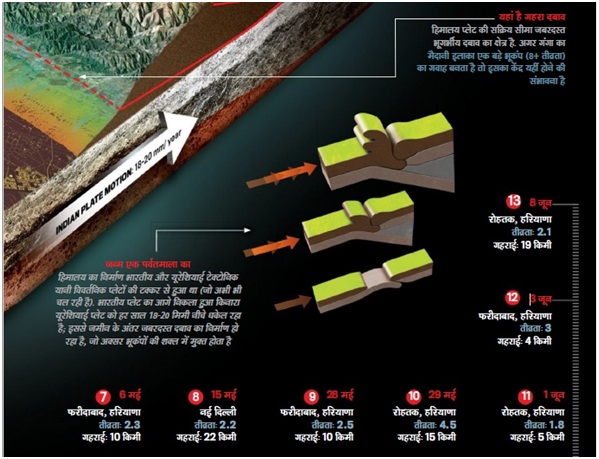
- Proximity to Himalayas : Delhi-NCR is not very far from the entire north-west and north-east Himalayan belt lies in the highest seismic potential zone V and IV, where major to great earthquakes can take place. The reason for earthquakes in Delhi lies in Earth’s distant past, when the Indian tectonic plate smashed into the Eurasian plate with such force that the crust folded upwards around the area of the collision, forming the Himalayan mountain range – home to the world’s tallest mountains. Studies have indicated that the Indian plate hasn’t come to rest, even though some 55 million years have passed, and is still moving into the Asian plate at 5-6 cm per year. One way geologists understand the consequences of this motion is in the form of ongoing mountain formation. Alongwith, due to this movement, many fault-lines (cracks) are formed in the Indo-Gangetic plain region like Mahendragarh-Dehradun Fault-line (the nearest fault-line from Delhi NCR). Strain energy is released through these faults or weak zones which accumulates as a result of northward movement of Indian plate and its collision with the Eurasian plate. Recent earthquakes of smaller magnitude in Delhi and its surrounding areas are the result of these phenomena.
- Concentration of more seismometers in and around Delhi : Out of the 115 detectors installed in the country, 16 are in or around Delhi,even more than the Himalayan region which is seismically much more active. As a result, even the earthquakes of smaller magnitude, those that are not even felt by most people, are recorded, and this information is publicly accessible in an easy manner.
Seismic Zones in India:
- Bureau of Indian Standards based on the past seismic history, grouped the country into four seismic zones, viz. Zone-II, Zone-III, Zone-IV and Zone-V.
- Of these, Zone V is the most seismically active region, while zone II is the least. The Modified Mercalli (MM) intensity, which measures the impact of the earthquakes on the surface of the earth, broadly associated with various zones is as follows:
Seismic Zone Intensity on MM Scale
II (Low intensity zone) : VI (or less)
III (Moderate intensity zone) : VII
IV (Severe intensity zone) : VIII
V (Very severe intensity zone) : IX (and above)
Seismic Zone Region
1. Zone V : Entire northeastern India, parts of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttaranchal, Rann of Kutch in Gujarat, parts of North Bihar and Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
2. Zone-IV : It covers the remaining parts of Jammu & Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh, Union Territory of Delhi, Sikkim, northern parts of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal, parts of Gujarat and small portions of Maharashtra near the west coast and Rajasthan.
3. Zone-III : It comprises of Kerala, Goa, Lakshadweep islands, remaining parts of Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat and West Bengal, parts of Punjab, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, Orissa, Andhra Pradesh, Tamilnadu and Karnataka.
4. Zone -II : It covers the remaining parts of the country.
Has the Government done anything to minimise the risks of Earthquakes?
- The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) has issued National Disaster Management Guidelines on Management of Earthquakes which contains roles and responsibilities of all stakeholders for effective management of earthquake disaster risk.
- NDMA also runs awareness campaigns on earthquakes through various means.
- Building Codes and Guidelines have also been published by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), Building Materials & Technology Promotion Council (BMTPC), Housing and Urban Development Corporation (HUDCO) and NDMA for the design and construction of earthquake resistant structures (as per Seismic Microzonation Maps) to minimize the loss of life and damage to property caused by earthquakes.
Way forward
- Can predicting Earthquake help ? Exact prediction of earthquake is not possible. What is important is that we need to make our structures earthquake resistant, we need to follow prescribed drills when an event happens, everyone must know what is the best place to run to when we are in office, or at home, or in open spaces.
- The only solution to minimise the loss of lives and properties is the effective preparedness against the earthquake like mock-drills and strictly following the Building Codes of earthquake resistance. Countries like Japan have proved this, where earthquakes are a common phenomenon yet the losses are negligible.
- Thus loss of life and damage of property due to earthquakes could be considerably reduced through proper planning and implementation of pre- and post-disaster preparedness and management strategies by respective State and Central Government agencies in a coordinated manner following the appropriate guidelines.
Connecting the dots
Question for Prelims
Recently, Delhi and its surrounding regions witnessed frequent occurrences of earthquakes of smaller magnitude. In this regard, consider the following statements :
1. India is mainly divided into 4 seismic zones in which Delhi lies in zone 3.
2. Ongoing formation of Himalaya is mainly responsible for occurrence of Earthquakes in and around the region of Delhi.
Which of the above statements is/ are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Question for Mains
“Unplanned urban construction and neglect of seismic microzonation might cause an unprecedented disaster in the event of a Bhuj-like earthquake in Delhi-NCR.” Comment.



