Why in the NEWS?
- The day of spring equinox 2025 was observed on 20th March.

Key Points:
- It marks the beginning of spring season in the Northern Hemisphere and the beginning of autumn season in the Southern Hemisphere.
- This day marks equality between the lengths of day and night, due to the Sun being directly above the equator.
What will you read next in this topic?
- What are equinoxes?
- What Happens on the Equinox?
- What is a solstice?
- Difference between Solstice and Equinox:
- Importance of Spring Equinox in Various Cultures
What are equinoxes?
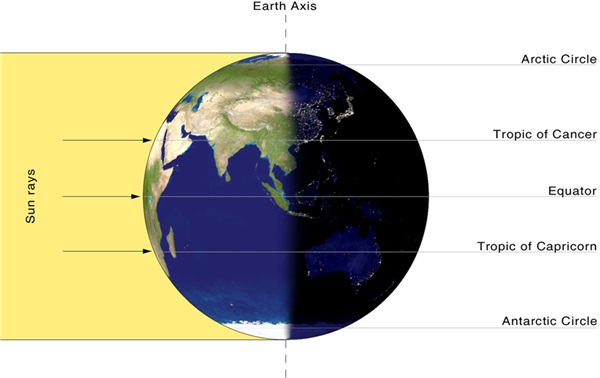
- Equinoxes occur twice a year, in March and in September.
- On these days, the Earth's axis and orbit are aligned so that both hemispheres receive the same amount of sunlight.
- On this day, the Sun is directly above the equator, and the length of day and night are equal.
- Both poles of the Earth receive equal sunlight at this time.
- March equinox: marks the beginning of spring in the Northern Hemisphere and fall in the Southern Hemisphere.
- September equinox: marks the beginning of autumn in the Northern Hemisphere and spring in the Southern Hemisphere.
- The word comes from the Latin words "aequus" (meaning equal) and "nox" (meaning night).
What Happens on the Equinox?
No Tilt of Earth's Axis:
- During the equinox, the Earth’s axis is not tilted toward or away from the sun.
- Unlike other times of the year when one hemisphere is tilted towards the sun (leading to longer days in that hemisphere), on the equinox, the tilt is minimal.
- This results in sunlight being distributed more evenly between the two hemispheres.
Equal Sunlight in Both Hemispheres:
- With the Earth’s axis nearly perpendicular to the sun’s rays, both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres receive nearly the same amount of sunlight.
- This is why, during the equinox, both hemispheres experience similar conditions in terms of daylight and night.
Equal Day and Night Lengths:
- Due to this alignment, the day and night lengths are almost exactly the same across the world.
- For most locations on Earth, the equinox means a day of roughly 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of night.
Slight Variations in Day and Night:
- Although the equinox is traditionally associated with equal day and night lengths, the exact balance may vary slightly.
- This is due to atmospheric refraction, which causes the sun to appear slightly above the horizon before it actually reaches the position directly above it.
- This effect causes the daylight to be a little longer than the night on the equinox.
What is a solstice?
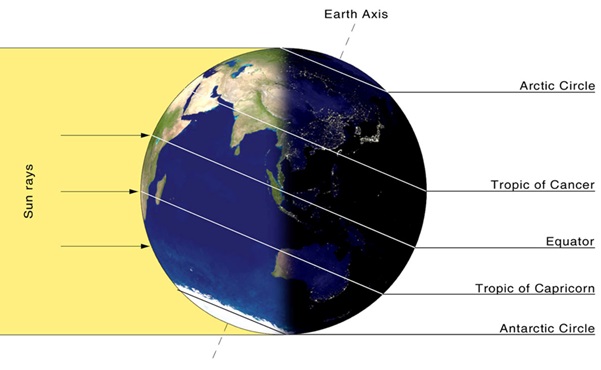
- A solstice is a day when the Earth's axis is tilted the most towards or away from the Sun, causing a disparity in the length of day and night in the Earth's two hemispheres.
- These days are particularly important because these are the days when we experience the longest and shortest days of the year.
Types of solstice:
- Summer Solstice (June 20-22)
- It is the longest day and shortest night of the year in the Northern Hemisphere.
- On this day, the Earth's northern hemisphere is tilted the most towards the Sun, causing maximum sunlight.
- During the summer solstice, the daytime is longest and the night-time is shortest in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Winter Solstice (December 20-23)
- It is the shortest day and the longest night of the year in the Northern Hemisphere.
- On this day, the Earth's northern hemisphere is tilted the most away from the Sun, causing minimum sunlight.
- During the winter solstice, the daytime is shortest and the night-time is longest in the Northern Hemisphere.
Difference between Solstice and Equinox:
Solstice:
- When the Earth is maximum tilted on its axis towards or away from the Sun, it is called a solstice.
- Due to this condition, the distribution of sunlight in both hemispheres of the Earth is uneven, and results in the longest and shortest days of the year.
- Summer Solstice (in June): The Northern Hemisphere has the longest day and the shortest night.
- Winter Solstice (in December): The Northern Hemisphere has the shortest day and the longest night.
Equinox:
- Equinox occurs when the Earth's axis is minimum tilted relative to the Sun, and both hemispheres receive sunlight equally.
- The length of day and night is equal on this day.
- Vernal Equinox (in March): It marks the beginning of spring in the Northern Hemisphere and autumn in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Autumn Equinox (in September): It marks the beginning of autumn in the Northern Hemisphere and spring in the Southern Hemisphere.
Importance of Spring Equinox in Various Cultures
- The spring equinox is not only important from a scientific point of view, but it is also celebrated in many cultures, most notably:
Persian New Year (Nowruz):
- It coincides with the spring equinox and is celebrated in many countries, including Iran.
- Nowruz begins on the spring equinox, the first day of Farvardin, the first month of the Iranian solar calendar.
Parsi community in India:
- Parsis celebrate Nowruz, which is associated with the spring equinox.
- This festival has been celebrated by followers of Zoroastrianism for over 3,000 years.
Japan:
- Japan has a national holiday on the day of the spring equinox, which reflects the importance of this day.
Easter (Christianity):
- In the Christian calendar, Easter is celebrated around the spring equinox, and it is the most important festival of Christianity.
- Its date changes every year, but it occurs around the spring equinox.
Passover in the Jewish calendar:
- The Jewish festival Passover is celebrated on the first full moon after the spring equinox.
- The Jewish New Year "Rosh Hashanah" and "Yom Kippur" also fall in this period.
Chuseok in Korea:
- In South Korea and North Korea, a large harvest festival called Chuseok is held on the autumn equinox, which is celebrated for three days.
|
Q. What is the effect of the Earth's tilt during the equinox?
(a) The Earth's tilt is at its maximum toward the sun.
(b) The Earth’s tilt is minimal, resulting in equal sunlight distribution.
(c) The Earth's tilt is at its maximum away from the sun.
(d) The tilt causes one hemisphere to experience a longer day than the other.
|

 Contact Us
Contact Us  New Batch : 9555124124/ 7428085757
New Batch : 9555124124/ 7428085757  Tech Support : 9555124124/ 7428085757
Tech Support : 9555124124/ 7428085757









