Prelims: Iraq is slowly sinking.
Mains: General Studies Paper-1, Important geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunamis, volcanic activity, cyclones etc., geographical features and their locations- Changes in critical geographical features (including water bodies and ice covers) and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes. |
Why in the NEWS?
- A mountainous region around the Zagros Mountains in Iraq is being pulled into the earth.

Key Points:
- The Earth is slowly sinking in the northern part of Iraq, particularly around the Zagros Mountains.
- A sinking oceanic "slab" beneath the Earth's surface is pulling the northern region of Iraq down with it.
- This phenomenon is not an immediate or emerging condition, but a long-term geological process that has been ongoing for millions of years.
- The scientific study of this phenomenon provides a deeper understanding of the dynamics inside the Earth and plate tectonics.
What will you read next in this topic?
- Why is Iraqi territory sinking?
- What are tectonic plates?
Why is Iraqi territory sinking?
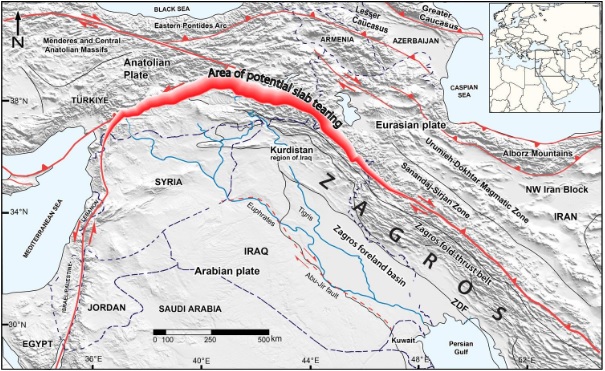
- In the northern part of Iraq, especially around the Zagros Mountains, a very slow, but important geological process is taking place in the Earth's surface, called plate tectonics.
- This phenomenon is happening mainly due to the dynamics between the Arabian and Eurasian continental plates.
Plate tectonics and the Neotethys oceanic slab
- There are several huge tectonic plates located on the Earth's surface, which collide with each other, merge into each other, or move away from each other.
- When the Arabian and Eurasian plates collide, a huge crack is formed, called the "Neotethys oceanic slab".
- This slab originated from the bottom of an ancient ocean that existed 66 million years ago.
- Now this slab is slowly sinking into the Earth's mantle (deep layer).
- This process is pulling Iraq's Zagros region down with it, causing this area of Iraq to slowly sink.
Zagros Mountains and Tectonic Collisions
- Iraq's Zagros Mountains were formed when the Arabian and Eurasian plates collided.
- The collision of these plates results in great stresses in the region, which cause the land beneath to sink or rise.
- In this process, the oceanic slab is slowly being subducted into the deeper part of the Earth, causing the earth around the Zagros Mountains to be pulled down as well.
Geological Research and Findings
- Koshanov and his team, using deep-Earth imaging and rock records, found that the Neotethys slab is indeed sinking.
- This research also revealed that the topography of the Zagros region is steeper than expected, a result of these tectonic collisions.
- This study helped us understand what role oceanic slabs beneath continental plates play when they collide and how these affect landforms.
- Mountain ranges such as the Zagros are a result of such collisions.
Earthquake prediction and impact
- The findings of this research also have practical implications, as they can help us understand the activities inside the Earth more accurately.
- Koshanov says that this study can help scientists create geological models that show the activities below the Earth's surface.
- Earthquakes are often caused by fractures or faults in layers of rocks.
- When tectonic plates collide with each other, stress and pressure are generated in these layers, which can cause earthquakes in the future.
- If scientists know more about these pressure fields, they can accurately predict the location, depth and intensity of earthquakes in the future.
Geothermal energy and heat production
- In addition, Koshanov says that this research can also estimate how much heat can be generated in the deep layers of the Earth, which can be used as geothermal energy in the future.
- To generate this type of energy, it is important that we understand where and at what depth in the inner layers of the Earth the temperature can be so high that it can be used for energy production.
Reference to the 2023 Turkey-Syria earthquake
- Finally, another important aspect of this research is that it can help create more accurate geological models, which can be helpful in predicting earthquakes in the future.
- In February 2023, large earthquakes in southern and central Turkey and northern Syria killed thousands of people and caused widespread damage.
- Such events prove that by studying these geological changes taking place in the Zagros region, scientists can help develop strategies to deal with such threats in the future.
What are tectonic plates?
- The outer layer of the Earth, called the "crust," is divided into many large and small parts, which we call tectonic plates.
- The movement and mutual movements of these plates cause the Earth's geologic events, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the formation of mountain ranges.
- These plates float on the Earth's inner structure, especially the mantle, and are constantly in motion.
Structure and Types of Tectonic Plates
- The Earth has a total of seven major tectonic plates, some of which cover entire continents, while some only cover oceanic areas.
- Along with these major plates, there are many smaller plates as well.
- African Plate
- Asian Plate (Eurasian Plate)
- Arabian Plate
- Intercontinental (Indo-Australian) Plate
- Pacific Plate
- North American Plate
- South American Plate
- The boundaries of these plates cause various types of motions and this is where events such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building occur.
Movement of Tectonic Plates
- The movement of tectonic plates is extremely slow, about 2 to 5 centimetres per year.
- However, their movement produces very large geological events.
- The movement of plates and the interaction between them leads to various types of geological processes:
- Diverging Boundaries: When two plates move away from each other, there is the formation of new crust. This process is mainly observed on the ocean floor.
- For example, the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
- Collision boundaries: When two plates collide, they may subduct beneath each other, or one plate may move above the other. This type of activity creates mountain ranges, such as the Himalayas.
- Side-sliding boundaries: When two plates slide past each other, this process can cause earthquakes. The San Andreas Fault is a prime example.
Events caused by tectonic plates
- Plate tectonics affects a variety of geological events, including:
- Earthquakes: When plates collide or move past each other, stress and pressure are generated. This pressure eventually breaks and manifests as earthquakes.
- Volcanic eruptions: When one plate subducts beneath another (subduction), the material there heats up and magma is formed. This magma rises and causes volcanic eruptions.
- Formation of mountain ranges: When two plates collide with each other, their edges rise up, forming mountain ranges. Such as the Himalayas, Andes Mountains, and the Rockies.
Effects of the movements of tectonic plates
- The movement of tectonic plates affects the Earth's geological phenomena, and these events not only lead to physical changes but also affect climate, life, and the environment:
- Earthquakes: Collisions between plates cause earthquakes, which can shake land and cause destruction.
- Rise or subsidence of the sea floor: Movement of plates can cause changes in the ocean floor, which affect beaches and ecosystems.
- Geothermal energy: Where plates collide, heat is generated, which can be useful for geothermal energy production. For example, the activities of volcanoes and geothermal energy production in Iceland are the result of the movement of these plates.
Important Plate Boundaries
- San Andreas Fault: This is a side-slipping boundary located in California. Here two plates slide past each other and the region is frequently subjected to earthquakes.
- Himalaya Mountains: This mountain range is formed due to the collision of Arabian and Eurasian plates. The collision of plates here has caused changes in the landform and the formation of mountains.
- Mid-Atlantic Ridge: This is a divergent boundary where two plates move apart in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean and the sea floor spreads.
|
Q. Which statement is correct about tectonic plates?
(a) Tectonic plates remain stable and never change.
(b) Tectonic plates are located in the outer layer of the Earth and are constantly moving.
(c) Tectonic plates are located only on the ocean floor.
(d) Tectonic plates have no effect on the Earth.
|


