
The Uttarakhand Public Service Commission has updated the UKPSC Syllabus. The UKPSC Syllabus provides the Uttarakhand Combined State Civil/ Upper PCS exam, an annual exam for entry level positions within Uttarakhand Civil Services. The UKPSC Exam Pattern comprises three key phases: Prelims, Mains, and Interviews. Before exam preparation, candidates must thoroughly familiarise themselves with the essential topics in the UKPSC Syllabus.
UKPSC Selection Process
Uttarakhand Combined State Civil/ Upper Subordinate Examination includes three levels sequentially. For instance-
- Prelims: Two Papers (Objective type)
- Main Examination: Eight Papers (Descriptive type)
- Interview
UKPSC Exam pattern Overview
The UKPSC examination is a multi-stage process designed to assess the knowledge and capabilities of candidates aspiring for various administrative positions in the state of Uttarakhand. Let us look at an overview of different stages that involves UKPSC Syllabus.
|
UKPSC Exam Pattern
|
|
Stages of UKPSC Exam
|
Subjects
|
Total Marks and Questions
|
|
Prelims Exam
|
Paper 1: General Studies 1
|
150 marks with 150 Questions
|
|
Paper 2: General Studies 2 (CSAT)
|
150 marks with 100 Questions
|
|
Mains Exam
|
General Hindi
|
150 marks
|
|
Essay
|
150 marks
|
|
General Studies 1
|
200 marks
|
|
General Studies 2
|
200 marks
|
|
General Studies 3
|
200 marks
|
|
General Studies 4
|
200 marks
|
|
General Studies 5
|
200 marks
|
|
General Studies 6
|
200 marks
|
|
Interview
|
Interview
|
150 marks
|
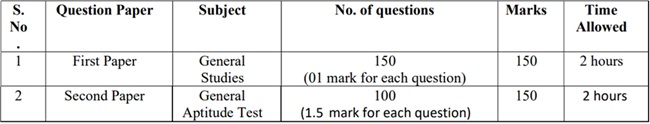
UKPSC Prelims Exam Pattern
- The UKPSC Prelims is only qualifying in nature, it is used as a filtering agent to weed out the non-serious candidates. The UKPSC Prelims comprised of two papers i.e., Paper I and Paper II. Both papers are of 150 marks with Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
- The preliminary examination will be objective type, in which the negative evaluation method will be adopted. For each wrong answer given by a candidate to a question one-fourth (1/4) mark of the marks prescribed for that question will be deducted.
- Merit list will be prepared on the basis of marks obtained in the first question paper (General Studies).
- Second question paper (General Aptitude Test) is a qualifying examination, in which it is mandatory to obtain 33% marks of all category/sub category candidates.
- Minimum 1/3 questions will be asked with the reference of state of Uttarakhand.
UKPSC Prelims Syllabus
Unit- 1
Indian History, Culture and National Movement
Pre-Historic Period
- Harappa Civilization, Vedic Civilization and Sangam Age Mahajanapadas and rise of Magadh; Religious Movements - Jainism, Buddhism, Bhagavatism and Shaivism; Persian and Greek Contacts and other related aspects.
Mauryan Empire
- Chandragupta Maurya, Ashoka and his Dhamma; Mauryan Administration, Economy, Society and Art; Kushanas and other related aspects.
Gupta Empire
- Foundation, Consolidation and Decline; Chandragupta I, Samudragupta, Chandragupta II, Skandagupta; Gupta Adminstration, Society, Economy, Literature and Art and other related aspects.
Post-Gupta Period
- Harshavardhan, Pal, Pratihara, Rashtrakuta, Chola, Pallava Chandel, Paramar, Chauhan; Social, Economic and Cultural Development between 650 A.D. and 1200 A.D and related other Aspect.
Advent of Islam in India
-
Iltutmish, Balban, Alauddin Khalji, Muhammad bin Tughlaq, Feroze Tughlaq, Sikandar Lodi and Ibrahim Lodi; Administration in Delhi Sultanate, Causes of decline of Delhi Sultanate, Society and Economy during Sultanate period, Indo-Islamic Architecture, Vijaynagar Empire, Sufism, Bhakti movement and other related aspects.
Mughal Empire
- Babar, Shershah Suri, Akbar, Shahjahan, Aurangzeb and decline of Mughal Empire, Mughal administration, Jagirdari and Mansabdari systems, Society and Economy during the Mughal period, Literature, Art and Architecture; Maratha, Sikh and Jat and other related aspects.
Advent of Europeans
- Portuguese, French, Dutch, British East India Company and British administration(1758-1857), British administration (1758-1857).
- Economic impact of British rule and other related aspects.
- Socio-religious Reform Movement during 19th Century. Viceroys of India (1858-1947) and other related aspects.
- First War of Independence (1857), Tribal, Non-Tribal, Caste and Peasant movements during 19 th and 20 th century; British administration after 1857 and other related aspects.
- Government of India Act 1858, Administrative and Judicial systems after 1858- Administration, Social, Educational, Judicial Reforms and other related aspects.
- Growth of Nationalism in India, Rise of National Movement.
Indian National Congress
- Foundation, Moderates and Extremists. Partition of Bengal, Swadeshi movement, Foundation of Muslim League, Surat Session and the split of Congress(1907), Morley-Minto Reform (1909).
First World War and Indian National Movement
- Home Rule Movement, Lucknow Pact (1916), August Declaration of 1917, Indian Revolutionary Movements in India and abroad. Beginning of Gandhian era, Government of India Act (1919), Rowlatt Act (1919), Jallianwala bagh Massacre (13 April, 1919), Khilafat Movement, Non Co-operation Movement Chauri-chaura- episode, Swaraj Party, Simon Commission, Nehru Report, 14th points of M.A. Jinnah, Lahore Session of Indian National Congress (1929), Civil Disobedience Movement, First Round Table Conference, Gandhi-Irwin Pact, Second and Third Round Table Conference, Communal Award and Poona Pact.
Government of India Act 1935
- Demand of Pakistan, Cripps Mission, Quit India Movement, Cabinet Mission Plan, Indian National Army, Interim Government, Mountbatten Plan, Indian Independence Act (1947), Partition of India, India after Independence, New activities and Related Organizations and other related aspects.
History and Culture of Uttarakhand
- Pre-historic Period.
- Proto-historic period.
- Ancient tribes of Uttarakhand.
- Kuninda and Yaudheya.
- Kartikepur dynasty.
- Kattyuri dynasty.
- Parmar dynasty of Garhwal.
- Chand dynasty of Kumaon.
- Gorkha Invasion and their rule in Uttarakhand.
- British Rule.
- Tehri Estate.
- Freedom Movement in Uttarakhand- First war of Independence (1857) and Uttarakhand.
- Role of Uttarakhand in India's national movement.
- People's movements of Uttarakhand.
- other related aspects.
Unit- 2
Indian and World Geography
Geography of world
- Important Branches, Earth and Solar System, Lithosphere, Latitudes, Longitudes, Time, Rotation, Revolution, Eclipses, Continents, Mountains, Plateaus, Planes, Hydrosphere, Lakes and Rocks, Atmospheric layers, Composition, Isolation, humidity. Oceanic relief, Currents, Tides, Temperature and Salinity.
- Agriculture, Plants, Insect, Livestock breeding, Power and Minerals, Resources, Industries, Population, Species and Tribes, Migration, Transport, Communication, International boundary line, Environment and World Trade (Regional Economic Group), Geographical Glossary and other related aspects.
Geography of India
- Geographic Introduction, Relief and Structure, Climate, Drainage system, Vegetation, Plants, Insect, Livestock breeding, Irrigation, Power, Soils, Water Resources, Agriculture, Minerals, Industries, Population and Urbanization, Transport, Communication System, Foreign Trade, Scheduled Caste/Tribes, Social ecologies, Domicile and Pollution and other related aspects.
Geography of Uttarakhand
- Geographical location, Relief and Structure, Climate, Drainage system, Vegetation, Wild life, Minerals, Agriculture, Animal Husbandry, Irrigation, Major Cities and Tourist Places, Populations , Schedule Caste/Tribes, Transport Network, Power Resource and Industrial development, Natural hazards and other related aspects.
Unit- 3
Indian Polity
National
- Parliamentary system
- Coalition Politics
- Regionalism, Casteism, Communalism, Terrorism and Naxalism
- Welfare : SC/ST/OBC’s and Minorities (with reference to constitutional provisions, legal framework, institutional arrangement, process and implications)
- Gender Politics (Equality, reservation, empowerment, welfare and safety/ security measures)
- Electoral reforms in India
- Governance : Institutions and process
- National integration
- Nuclear policy of India
- Environmental Concerns
- Economic and financial reforms: Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization (LPG) and its impact on politics and governance; planning machinery and planning process and banking sector (RBI, NABARD and IDBI etc)
- Institutional reforms in India like MNREGA, NRHM, JNNURM etc., Public private partnership (PPP) mode.
- Citizen Participation in Political and Administrative processes of the country
- Civil society
- Lok pal and Lok Ayukt
- Other related aspects.
International
- United Nations
- International Organization
- Environmental concerns at global level
- SAARC, ASEAN, SAFTA and another regional groups
- India’s Approach to major world issues: Disarmament, Human Rights and Globalization
- BRICS and its importance for India
- Other related aspects
Constitution of India
- Constitutional Development in India
- Constituent Assembly
- Preamble
- Basic Features of Indian Constitution (Including its various parts, Important articles and schedules)
- Fundamental Rights and Duties
- Directive Principles of State policy
- Constitutional Amendment method and important constitutional amendments
- Federal and Parliamentary system of Governance in India
- Parliamentary Committees (Public Accounts committee, Estimate Committee and Joint Parliamentary Committee)
- Constitutional Bodies : Election Commission and Comptroller and Auditor General
- Judiciary : Supreme Court and High Courts
- Other related aspects
Indian Polity
- Union Executive : President, Prime Minister and Council of Ministers, Cabinet Secretariat, Central Secretariat and PMO
- State Executive : Governor and Chief Minister and Council of Ministers, State Secretariat and Chief Secretary
- Union Parliament and State Legislatures in India
- Election Machinery and Process
- Political Parties and Pressure Groups
- Politicians and Civil servant Relationships
- Development of Political Culture in India
- Agencies of Political socialization
- Evolution and Growth of Administrative system in India
- Re-organization of states in India
- Administration of Union Territories and other specified states and areas in India
- Administrative reforms (including various important Committees and Commissions)
- District Administration
- Other related aspects
Panchayati Raj
- Local Governance : 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment Acts
- State Finance Commission : Functions and Role
- Devolution of powers to local bodies
- Types of local bodies in India : Municipal corporations, Municipal councils, Nagar Panchayat,
- Gram Panchayat, Panchayat Samities and Zila Parishad
- Other related aspects
Public Policy
- Good Governance : Citizen Charter and E-Governance
- Prevention of Corruption and Lok Pal and Lok Ayuktas
- Right to Information
- Right to Education
- Right to services
- Other related aspects
Issues Concerning Rights
- Fundamental Rights
- Protection of Civil Right Act, 1955
- Various rights pertaining to protection of SCs, STs, Issues related Minorities, Women and Children and Old persons in India
- Other related aspects.
Political System of Uttarakhand :-
Governance, Governor, Legislation, Chief Minister, Council of Ministers, Central State Relation, Public Services, Public Service Commission, Auditing, Advocate General, High Court and its jurisdiction, Provision for minorities, Schedule Caste/Tribes, Special State Selection Criteria, Official Language, Consolidated fund and Contingency Fund, Political Parties and Election, Local Government and Panchayati Raj, Community Development, Public Policy, Right Related Issues (Education, Employment, Development etc.) Governance (Prevention of Corruption, Lok Ayukt, Citizen charter, E-Governance, Right to Information, Samadhan Yojna etc.) and other related aspects.
Unit – 4
Economic and Social development
National
- Economic Policy : Economic Reforms in India, Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization.
- Foreign Direct Investment (F.D.I), Inflation, Inclusive Growth, Economic development v/s Environmental conservation.
- Programmers for eradication of poverty and unemployment. Human Development Index (H.D.I).
- Census and Main features of India and population. Population and Economic Development. Issues related to urbanization.
- Main features of the union budgets.
- Main features of the economy of India.
- Natural and energy resources of India, Trade (with external sector), Commerce, Industries, Schemes and Projects and direction of Economic Growth.
- Tax reform and and Banking Business.
- Planned Development.
- National Development Council.
- National Income.
- Indian Agriculture (Agricultural productivity, Livestock, Green Revolution, Food Security, Food grain prices, Buffer stock, Agricultural Policy, Agricultural/Seed crop insurance scheme).
- Indian Financial/Money/Capital/Security Market.
- Insurance sector, Tax structure, Public finance and fiscal policy.
- Concepts (Rolling plan, Sweat shares, Hawala, Gilt edge market, Black market, Black money etc.).
- Other related aspects.
International
- World Trade Organization (W.T.O) International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD). International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, South Asian Association for Regional Co-operation (SAARC). Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN). South Asian Preferential Trade Agreement (SAPTA), BRICS, OPEC and Other regional Economic and commercial organizations.
- International flow of capital, human resources and technology.
- Foreign Exchange Regulation Act (FERA). Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA). Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA).
- World Human Development Index.
- Glossary.
- Other related aspects.
Uttarakhand
- Main Features of economy and budgets, Natural and energy resources, Trade, Commerce, Industries, Schemes and Projects, Tax and economic reforms, Planned development, Agriculture, Live Stock, Food security, Public Finance and fiscal Policy, Census, Human Development Index, Tourism, Role of herbs and culture in the economic development. Other related aspects.
Unit -5
General Science and Technology:
- Question on General Science will cover general appreciation and understanding of Science including matters of every day observation and experience, as may be expected of a well educated person, who has not made a special study of any scientific discipline.
- Science and Technology in India: History and contribution.
Current affairs
- National and International Awards, Prizes, Discoveries, Inventions, Science Congresses, Conferences, Solar technology, Application of new technology for human welfare, health and medicines, Environmental Awareness, Natural Bio resources, etc. State, National and International Scientific and Research Related other organizations IUCN , WWF, IPCC, WHO, UNESCO, etc. Information technology and application of computers in daily life, e-governance, etc.
Ecology and environment
- Habitat, community ecosystem, Structure and function, adaptations. Plants and their partition, Traditional agriculture, Commercial agriculture and Commercialization of agriculture, Production of agricultural crops and their regional distribution (State, National and International Level ) , Problems in agriculture field, Agricultural diversity, etc.
- Natural resources – Soil, water, air, forests, grasslands, wetlands, marine. Planning and management of Renewable and non-renewable energy resources.
- Biodiversity – Threats and conservation. Ethics and usage
- Environmental Crisis: Air, water, soil and space pollution. Laws and Acts, Global warming .
- Global climate change – Causes and effects.
Concept of remote sensing and GIS Applications.
Weather Forecasting.
Application of spreadsheet and Database Applications.
Physical Science/Awareness
- Fundamentals of Computer and Information processing, Basic Computer organization, Boolean Algebra, Logic Gates, Problem solving Techniques and Computer Languages, Business data processing, Data Communication and Computer Networks and security, use of Internet and multimedia applications, Cloud computing, Application of PC, Software Packages, Basics of cyber law, etc.
- Matter and its States, acids, bases and salts, origin and distribution of element, hard and soft water, heavy water, purification, batteries, fuel cells, corrosion, nuclear fission and fusion, elements of symmetry, polymers, carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, lipid, hormones, vitamins, medicines and healthcare, dyes, cosmetics, food chemistry, etc.
- Mechanics, General properties of matter, Wave motion , Sound and electromagnetic waves, Heat, Light, Magnetism, Electricity, Atomic & Nuclear Physics, Astronomy and space physics. X-rays and semiconductor technology etc.
Life Science
- Branches, contribution, Natural Resources and their management. Biodiversity, Biotechnology, Nanotechnology, Bio products, Vaccines, Immunization, Health care, Genetically modified organisms, Global warming and climate change, Livestock breeding, Plants and Human welfare etc.
Scientific Glossary
- Natural Resources of Uttarakhand and their contribution to National and International Climate change, etc.
Unit -6
Current events of State, National and International Importance
- Continents and Nations, Important events of Space, Wonders of the World, Religions of the World, Indian States, Famous books and writer of the World/India, Famous Scientists, Important Awards, Indian defense system, Health and Family welfare, Scientific and technical development, Education, National symbols, Protocol in India, Important Human rights and welfare organizations of World/India, Important Religious places, Important Passes, Dances of India, Cultural Institutes, Music, Drawing, Indian Languages, World Heritage, Important newspapers, Important Dates, Sports Landscape, Important Sports and related terms, Conventions/Exhibitions/Festival/Conferences, Important Reports and other related aspects.
Second paper -General Aptitude Test
Unit – 1
- Aptitude – Statement/propositions true and false statement (syllogism) Analogies, Similarities and differences, Observation.
- Communication and Inter personal Skills, Word building, Coding decoding, Numerical Operations.
- Logical and Analytical ability
- Logic : Statements- Arguments, Statement- Assumptions, Statement- Courses of Action,
- Statement – Conclusions, Deriving Conclusions from passages, Theme Detection, QuestionStatements, Ven Diagram, Arithmetic number series, Arithmetical reasoning and Figural
- Classification, Relationship concepts.
- Decision – making and problem solving, Decision-making, Visual memory, Discrimination, assertion and Reason.
- General mental Ability: direction sense Test, Social Intelligence, Emotional Intelligence, Critical thinking, Puzzle Test, Alphabet test, Data sufficiency, Inserting the missing Character.
- Numerical identification- Number & their classification, test of divisibility of number, general properties of divisibility, test of prime number, division and remainder, remainder rules, two-line number series, sum rules on natural numbers.
- Statistics Analysis- Presentation of Data through chart, graph, Tables, sufficiency of data
Unit – 2
अंग्रेजी भाषा में बोधगम्यता कौशल
- There shall be a long passage in English for comprehension, followed by three objective-type questions, with multiple choices, of 1.5 mark each. These questions will test the candidate’s ability to comprehend the ideas contained in the passage as well as his/her knowledge of English language/grammar.
- The four questions (1.5 mark each) based on language/grammar may cover the following areas:
- Vocabulary
- Antonyms
- Synonyms
- One-word substitution
- Phrases/phrasal verbs
- Transformation of sentences
हिन्दी भाषा में बोधगम्यता कौशल-
-
- हिन्दी भाषा में बोधगम्यता कौशल हेतु दिए गए विस्तृत अपठित गद्यांश या अवतरण से, प्रतिपाद्य (विषयवस्तु), भाषा और व्याकरण पर आधारित, 06 वस्तुनिष्ठ प्रश्न पूछे जाएंगे। प्रत्येक वस्तुनिष्ठ प्रश्न डेढ़ अंक का होगा तथा प्रत्येक प्रश्न के चार वैकल्पिक उत्तर A, B, C, D होंगे। जिनमें केवल एक उत्तर ही सही होगा।
- 07 वस्तुनिष्ठ प्रश्न (प्रत्येक डेढ़ अंक) अपठित गद्यांश के कथ्य, शीर्षक उद्देश्य, भाषा, लोकोक्ति एवं मुहावरा, अलंकार, शब्द- विवेक (तत्सम, तद्भव, देशज एवं विदेशी शब्द, पर्यायवाची शब्द, विलोम शब्द, शब्दार्थ), उपसर्ग, प्रत्यय, सन्धि, समास और क्रियारूप आदि पर आधारित होने चाहिए।
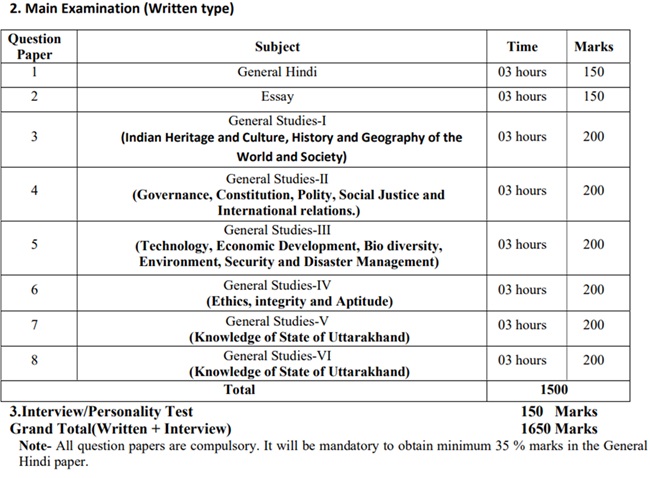
UKPSC Mains Exam Pattern
Candidates who qualified for the UKPSC prelims exam are called for the mains exam. The marks of the mains exam will be considered for the final selection of the candidates. The UKPSC Mains Exam comprises of eight descriptive papers. The UKPSC Mains Exam is a merit-deciding round, it holds a great weightage as it is of 1500 marks.
UKPSC Mains Syllabus
The UKPSC Mains Exam comprises eight papers. The marks secured in the UKPSC main exam are the deciding factor in the final selection.
1. सामान्य हिंदी

2. Essay
This question paper will consist of three sub-sections-‘A’,‘B’ and ‘C’. The candidates will have to write an essay of 700-800 words limit from each sub section of opted language alternatives.
Section :- A
- Literature and Culture
- Social sphere.
- Political sphere.
- Economic sphere : Agriculture, Industry and Trade.
Section :- B
- Science, Environment and Technology
- National and International Events
- Natural Calamities : Landslide, Earthquake, Deluge, Drought, etc.
- National Development Programmes and projects.
Section :- C
- Social structure of Uttarakhand.
- History and Culture, Art and Literature in Uttarakhand.
- Economic and Geographic Scenario of Uttarakhand, Tourism and Migration in Uttarakhand.
- Environment & Disaster and Disaster Management in Uttarakhand.
- Women Empowerment in Uttarakhand.
Note: The Maximum Marks for the essay of 700-800 words limit from each section will be 50. The marks during evaluation of each essay will be given keeping in the mind the following points.
- Accuracy of Language and Grammar, Proper Word Selection, and Legible Handwriting.
- Rendering of Original Thoughts related to the Subject.
- Presentation of Multi-dimensional and Comprehensive Understanding of the Subject.
- Systematic, Compatible, and Reasonable Revelation of Subject related thoughts and Essay Style.
- Clarity, Expression Ability and Expansion and Summarization ability with reference to the given subject.
3. GENERAL STUDIES-I
(Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of the World and Society)
- Indian culture will cover the salient aspects of art Forms, literature and Architecture from ancient to modern times.
- Modern Indian history from about the middle of the eighteenth century until the present – significant events, personalities, issues.
- The Freedom Struggle – its various stages and important contributors/contributions from different parts of the country.
- Post – independence consolidation and reorganization within the country.
- History of the world will include events from 18th century such as industrial revolution, world wars, re-drawal of national boundaries, colonization, decolonization, political philosophies like communism, capitalism, socialism etc.- their forms and effect on the society.
- Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India.
- Role of women and women’s organization, population and associated issues, poverty and developmental issues, urbanization, their remedies.
- Effects of globalization on Indian society.
- Social empowerment, communalism, regionalism & secularism.
- Salient features of word’s physical geography.
- Distribution of key natural resources across the world (including South Asia and the Indian subcontinent); factors responsible for the location of primary, secondary, and tertiary sector industries in various parts of the world (including India).
- Important Geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclone etc., geographical features and their location – changes in critical geographical features (including water-bodies and ice-caps) and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes.
4. GENERAL STUDIES – II
(Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International relations)
- Indian Constitution- historical underpinnings, evolution, features, amendments, significant provisions and basic structure.
- Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges significant provisions to the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein.
- Separation of powers between various organs dispute redressal mechanisms and institutions.
- Comparison of the Indian constitutional scheme with that of other countries.
- Parliament and State legislatures – structure, functioning, conduct of business, powers & privileges and issues arising out of these.
- Structure, organization and functioning of the Executive and the judiciary – Ministries and Departments of the Government; pressure groups and formal /informal associations and their role in the polity.
- Salient features of the Representation of people’s Act.
- Appointment to various Constitutional posts, powers, functions and responsibilities of various Constitutional Bodies.
- Statutory, regulatory and various quasi-judicial bodies.
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Development processes and the development industry – the role of NGOs, SHGs, various groups and associations, donors, charities, institutional and other stakeholders.
- Welfare schemes for vulnerable sectional of the population by the Centre and states and the performance of these schemes; mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections.
- Issues relating to development and management of social / services relating to health, Education, human Resources.
- Issues relating to poverty and hunger.
- Important aspects of governance, transparency and accountability,e–governance applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential; citizens charters, transparency & accountability and institutional and other measures.
- Role of civil services in a democracy.
- India and its neighborhood – relations.
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and / or affecting India’s interests.
- Effect of policies and politics of developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora.
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora – their structure, mandate.
5. GENERAL STUDIES – III
(Technology, Economic Development, Bio diversity, Environment, Security and Disaster Management)
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
- Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
- Government Budgeting.
- Major crops-cropping patterns in various parts of the country, - different types of irrigation and irrigation systems storage, transport and marketing of agricultural produce and issue and related constraints; e – technology in the of farmers.
- Issue related to direct and indirect farm subsidies and minimum support prices; public
- Distribution System – objectives, functioning, limitations, revamping; issues of buffer stocks and food security; Technology missions; economics of animal – rearing.
- Food processing and related industries in India – scope’ and significance, location, upstream and downstream requirements, supply chain management.
- Land reforms in India.
- Effects of liberalization on the economy, changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth.
- Infrastructure: Energy, ports, Airports, Railways etc.
- Investment models.
- Science and Technology – developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
- Achievements of Indians in science & technology; indigenization of technology and developing new technology.
- Awareness in the fields of IT, Space Computers, robotics, nano – technology, bio – technology and issues relating to intellectual property rights.
- Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
- Disaster and disaster management.
- Linkages between development and spread of extremism.
- Role of external state and non-state actors in creating challenges to internal security.
- Challenges to internal security through communication networks, role of media and social networking sites in internal security challenges, basics of cybers security; money – laundering and its prevention.
- Security challenges and their management in border areas – linkages of organized crime with terrorism.
- Various Security forces and agencies and their mandate.
6. GENERAL STUDIES – IV
(Ethics, integrity and Aptitude)
- This paper will include questions to the candidates’ attitude and approach to issues relating to integrity, probity in public life and his problem-solving approach to various issues and conflicts faced by him in dealing with society. Questions may utilize the case study approach to determine these aspects. The following broad areas will be covered :
- Ethics and Human Interface : Essence, determinates and consequences of Ethics in – human actions; dimensions of ethics; ethics – in private and public relationships. Human values – lessons from the lives and teachings of great leaders, reformers and administrators; role of society and educational institutions in inculcating value.
- Attitude : content, structure, function; its influence and relation with thought and behavior; moral and political attitudes; social influence and persuasion.
- Aptitude and foundational values for civil service, integrity, impartiality and – partisanship, objectivity, dedication to public service, empathy, tolerance and compassion towards the weaker – sections.
- Emotional intelligence – concepts, and their utilities and application in administration and governance.
- Contributions of moral thinkers and philosophers from India and world.
- Public/Civil service values and Ethics in public administration: Status and problems; concerns and dilemmas in government and private institutions; laws, rules, regulations and conscience as sources of ethical guidance; accountability and ethical governance; strengthening of ethical and moral values in governance; ethical issues in international relations and funding; corporate governance.
- Probity in Governance: Concept of public; philosophical basis of governance and probity; Information sharing and transparency in government, Right to information, Codes of Ethics, Codes of Conduct, Citizen’s Charters, Work culture, Quality of service delivery, Utilization of public funds, challenges of corruption.
- Case studies on above issues.
7. GENERAL STUDIES – V
(Knowledge of State of Uttarakhand)
- History of Uttarakhand - Prehistoric period, Proto-historic period, Major archeological sites of Uttarakhand, Ancient tribes of Uttarakhand, Kunindas and Yaudheyas, Katyuri dynasty, Parmar dynasty in Garhwal- Rule, Administration, society, Economy, Chand dynasty of Kumaon- Rule, Administration, society, Economy, Gorkha invasion and administration in Uttarakhand.
- British Rule in Uttarakhand- Administrative System, Land Revenue, Forest Management, Economy, Education and Health System, Growth of Vernacular journalism in Uttarakhand, Tehri state- Rule, Administration, Society, Economy, Religion and Culture, National Movement, Prominent Freedom Fighters of Uttarakhand, Merger of the Tehri state.
- Popular Movements in Uttarakhand- Coolie Begar Movement, Dola Palki Movement, Chipko Movement, Anti-Liquor Movement, Social Reformers of Uttarakhand. Anti princely Tehri State, Movement of separate Uttarakhand state and its immediate and long-term consequences.
- Society and Culture of Uttarakhand- Family, Marriage and kinship system Uttarakhand, Caste system and caste mobility in Uttarakhand: Scheduled Caste, Scheduled Tribes and Others Backward Classes in Uttarakhand; Rural Power Structure, Urbanization and Industrialization in Uttarakhand, Folks Songs, Folks dance and craft.
- Prominent Folks singers and folks artists of Uttarakhand, musical instruments, paintings, costumes, food habits, Religious places and Temples of Uttarakhand, Fairs and Festivals, Dialects and craft of Uttarakhand.
- Uttarakhand State- Political, Local Administration and Public Policy; Political System in Uttarakhand, Party Politics, Regional Parties, Pressure groups.
- Administrative system- Structure of the state government, Cabinet and Departments, Administrative Agencies and District and Tehsil level Administration. State Public Service Commission. Lok Ayukta, State Vigilance Agency. Local Self Government in
- Uttarakhand- Nature of urban local bodies and Panchayati Raj institutions in
- Uttarakhand, State Finance Commission, State Election Commission. Public Policy in
- Uttarakhand- Good governance- Citizen's Charter and e-governance, prevention of corruption and Lok pal and Lokayukta, Right to information, Right to education, Right to service, Women Empowerment, MNREGA, Soldier’s Welfare and rehabilitation etc. Important Ayog in Uttarakhand.
- Current events in the context of Uttarakhand state.
8. GENERAL STUDIES – VI
(Knowledge of State of Uttarakhand)
- Geography of Uttarakhand- Location, Extent and Strategic Importance, Structure and relief, Climate, Drainage System, Natural Vegetation, Soil, Glacier, Lake and Climate Change. Resources- Forest, Water, Minerals and Land, Agriculture, Irrigation, Horticulture, Animal Husbandry, Industry. Transport – Road, Rail and Air. Hydro-electric Projects, Water Scarcity and Solution.
- Tourism – Problems and Prospects.
- National parks and Wild-life sanctuaries.
- Population- Growth Rate, Density, Distribution, Sex Raito, Literacy, Migration- Pattern, Problem and solution. Rural Settlement- type and patterns, Urbanization and cities, Smart City. Tribal habitat, Human Development Index.
- Economy of Uttarakhand- Main features of the state's economy.
- Natural Resources - Water, Forests, Minerals etc.
- Economic profile of the State- State domestic products and its Components, Per Capita Income. Major sources of income; Agriculture, Horticulture, Medicinal Plants, Forest products, and Tourism etc.
- Industrial development: State MSME Policy, Large, Medium, Small, Cottage and Handicraft Industries, Investment scenario, Problems and Possibilities.
- Infrastructure : Physical – Road, Rail and Air transport, Banking and financiInstitutions, Education Health, Energy, Communication, Self Help Groups(SHGs).
- Economic Planning and Policies – State annual plans, Development Programmes, Schemes and Policies; Decentralized Planning- Panchayati Raj Institutions and Urban Local Bodies.
- Public Finance : Revenue receipts, State Taxes, Public Expenditure, Uttarakhand’s Budget.
- Major economic problems of the State – Poverty, Migration, Natural Disasters, Environmental degradation.
- Welfare programs- Youth, Child and Women welfare programs, Poverty alleviation programs, MNREGA, Food and Civil supply, soldiers welfare and rehabilitation etc.
- Disaster Management: Nature, types and effect Important Factors of natural disaster and efforts to reduce it. Denudation, Earthquake, Cloud-burst, Forest Fire, Drought & Avalanche etc. Difficulties in disaster Management.
- Ecological – Sensitive areas. Role of NDRF and SDRF.
- Disaster Management Act-2005, National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA).
- Disaster and impact due to Anthropogenic activites. Efforts of Uttarakhand Government.
- Human Resource and Community Development in Uttarakhand- Employment and
- Development: Human resource management and human resource development and its indicators in Uttarakhand. Nature and types of unemployment problem in Uttarakhand. Uttarakhand government schemes. Rural development and community development schemes – role of related institutions and organizations including centrally and state sponsored schemes.
- Education - Role of education in human resource development and social change.
- System of education in Uttarakhand - problems and issues (including universalization
- and professionalization), education for women and other socially and economically
- deprived sections and minorities.
- Right to Education, Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan and National Secondary Education Abhiyan
- in Uttarakhand. Status of higher, technical and professional education in Uttarakhand.
- Role of various institutions (including Centre, State and other organizations) in the
- improvement of education.
- Health as a component of human resource development in Uttarakhand-
- Health care system in Uttarakhand.
- National Rural Health Mission and other related schemes.
- Health and Nutrition.
- Food Security Act etc.
UKPSC Interview
The UKPSC Interview is the last exam phase. Candidates who qualify Mains exam will be called for the Personnel Interview. The Interview will be of 150 Marks. The objective of the interview is to check the personal suitability of the candidate, communication skills, decision-making abilities, and knowledge of current affairs, governance, and ethics. The interview panel tries to understand the candidates' views on social issues, their approach to problem solving and their readiness to assume the responsibilities of the civil service.



